Genetic ablation of the fatty acid-binding protein FABP5 suppresses HER2-induced mammary tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23722546
- PMCID: PMC4082958
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0384
Genetic ablation of the fatty acid-binding protein FABP5 suppresses HER2-induced mammary tumorigenesis
Abstract
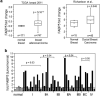
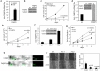
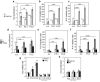
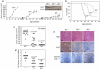
The fatty acid-binding protein FABP5 shuttles ligands from the cytosol to the nuclear receptor PPARβ/δ (encoded for by Pparδ), thereby enhancing the transcriptional activity of the receptor. This FABP5/PPARδ pathway is critical for induction of proliferation of breast carcinoma cells by activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). In this study, we show that FABP5 is highly upregulated in human breast cancers and we provide genetic evidence of the pathophysiologic significance of FABP5 in mammary tumorigenesis. Ectopic expression of FABP5 was found to be oncogenic in 3T3 fibroblasts where it augmented the ability of PPARδ to enhance cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. To determine whether FABP5 is essential for EGFR-induced mammary tumor growth, we interbred FABP5-null mice with MMTV-ErbB2/HER2 oncomice, which spontaneously develop mammary tumors. FABP5 ablation relieved activation of EGFR downstream effector signals, decreased expression of PPARδ target genes that drive cell proliferation, and suppressed mammary tumor development. Our findings establish that FABP5 is critical for mammary tumor development, rationalizing the development of FABP5 inhibitors as novel anticarcinogenic drugs.
©2013 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fatty acid binding protein 5 promotes metastatic potential of triple negative breast cancer cells through enhancing epidermal growth factor receptor stability.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):6373-85. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3442. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25779666 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin restores sensitivity to retinoic acid in triple negative breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2014 Sep 27;14:724. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-724. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25260874 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid-binding protein 5 and PPARbeta/delta are critical mediators of epidermal growth factor receptor-induced carcinoma cell growth.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 18;285(25):19106-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099770. Epub 2010 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20424164 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid activation of peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor delta represses obesity and insulin resistance.Nutr Rev. 2010 Jan;68(1):67-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00261.x. Nutr Rev. 2010. PMID: 20042001 Review.
-
The emerging role of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) in cancers.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Jul;28(7):103628. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103628. Epub 2023 May 23. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37230284 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic comparison of primary bovine horn core carcinoma culture and parental tissue at early stage.Vet World. 2017 Jan;10(1):38-55. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.38-55. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28246447 Free PMC article.
-
4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl retinate inhibits proliferation, invasion, and migration of breast cancer cells by independently regulating CRABP2 and FABP5.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Apr 27;12:997-1008. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S151029. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. Retraction in: Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 03;18:2713-2714. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S484570. PMID: 29731607 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Structural basis for ligand regulation of the fatty acid-binding protein 5, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ (FABP5-PPARβ/δ) signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 23;289(21):14941-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514646. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24692551 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 inhibits tumor growth by two distinct mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):34065-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.604041. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25320093 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-sensors, enigmatic-orphan and orphan nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in breast-cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42661-42682. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7410. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26894976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pang J, Liu WP, Liu XP, Li LY, Fang YQ, Sun QP, et al. Profiling protein markers associated with lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer by DIGE-based proteomics analysis. Journal of proteome research. 2010;9:216–26. - PubMed
-
- Adamson J, Morgan EA, Beesley C, Mei Y, Foster CS, Fujii H, et al. High-level expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein in prostatic carcinomas and its effect on tumorigenicity. Oncogene. 2003;22:2739–49. - PubMed
-
- Morgan EA, Forootan SS, Adamson J, Foster CS, Fujii H, Igarashi M, et al. Expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein (C-FABP) in prostate cancer: potential prognostic marker and target for tumourigenicity-suppression. International journal of oncology. 2008;32:767–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

