Role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in a 'two-hit' model of hypoxia and oxidative stress in human A549 epithelial cells in vitro
- PMID: 23722590
- PMCID: PMC3776717
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1397
Role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in a 'two-hit' model of hypoxia and oxidative stress in human A549 epithelial cells in vitro
Abstract
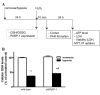
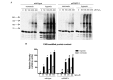
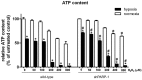
A preceding hypoxic insult can sensitize the cells or the organism to a subsequent, second insult. The aim of the present study was to investigate the molecular mechanism of this phenomenon (often termed 'two-hit' injury paradigm), in an in vitro model of hypoxia/oxidative stress injury in A549 epithelial cells, with special emphasis on the role of the nuclear enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in the process. Pre-exposure of the cells to 24 h hypoxia significantly reduced intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels, reduced mitochondrial activity and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels. However pre-exposure to hypoxia failed to induce any change in PARP-1 expression and activation, DNA single‑strand breaks or plasma membrane integrity. Pre-exposure to hypoxia markedly increased the sensitivity of the cells to subsequent oxidative stress-induced DNA damage. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced a concentration-dependent increase in DNA breakage, PARP activation, depletion of intracellular ATP, inhibition of mitochondrial activity and two distinct parameters that quantify the breakdown of plasma membrane integrity (propidium iodide uptake or lactate dehydrogenase release). PARP-1 activation played a significant role in the H2O2-induced cell death response because PARP activation, depletion of intracellular ATP, inhibition of mitochondrial activity, and the breakdown of plasma membrane integrity were attenuated in cells with permanently silenced PARP-1. Based on measurement of the endogenous antioxidant GSH, we hypothesized that the mechanism of hypoxia-mediated enhancement of H2O2 involves depletion of the GSH during the hypoxic period, which renders the cells more sensitive to a subsequent DNA single‑strand break elicited by H2O2. DNA strand breakage then activates PARP-1, leading to the inhibition of mitochondrial function, depletion of ATP and cell necrosis. PARP-1 deficiency protects against the cytotoxicity, to a lesser degree, by protecting against GSH depletion during the hypoxic period, and, to a larger degree, by maintaining mitochondrial function and preserving intracellular ATP levels during the subsequent oxidative stress period.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is a survival mechanism in cigarette smoke-induced and hydrogen peroxide-mediated cell death.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Nov 1;53(9):1680-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.579. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22964577
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and PARP Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Role in Cardiovascular Disorders.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018 Dec;18(6):493-506. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9462-2. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29968072 Review.
-
Caffeine metabolites are inhibitors of the nuclear enzyme poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 at physiological concentrations.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 28;72(7):902-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.023. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16870158
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 protects neurons against apoptosis induced by oxidative stress.Cell Death Differ. 2007 Jun;14(6):1211-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402117. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Cell Death Differ. 2007. PMID: 17347665
-
Neuronal trauma model: in search of Thanatos.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2004 Nov;22(7):485-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.07.015. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15465278 Review.
Cited by
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in cellular senescence.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Aug;97(8):2089-2109. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03540-1. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37335314 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Protection by PARP Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 16;21(8):2767. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082767. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32316192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of hypoxia-related genetic polymorphisms on the prognosis of patients with metastatic gastric cancer treated with EOF.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):1334-1342. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7414. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29399184 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Cellular Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on Human Lung Cancer Cells: Potential Therapeutic Implications.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1908164. doi: 10.1155/2016/1908164. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27375834 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rotstein OD. Modeling the two-hit hypothesis for evaluating strategies to prevent organ injury after shock/resuscitation. J Trauma. 2003;54:S203–S206. - PubMed
-
- West MA, Li MH, Seatter SC, Bubrick MP. Pre-exposure to hypoxia or septic stimuli differentially regulates endotoxin release of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, interleukin-1, prostaglandin E2, nitric oxide, and superoxide by macrophages. J Trauma. 1994;37:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Brehmer F, Bendix I, Prager S, van de Looij Y, Reinboth BS, Zimmermanns J, Schlager GW, Brait D, Sifringer M, Endesfelder S, Sizonenko S, Mallard C, Bührer C, Felderhoff-Mueser U, Gerstner B. Interaction of inflammation and hyperoxia in a rat model of neonatal white matter damage. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49023. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

