Dual bronchodilation with QVA149 versus single bronchodilator therapy: the SHINE study
- PMID: 23722616
- PMCID: PMC3844137
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00200212
Dual bronchodilation with QVA149 versus single bronchodilator therapy: the SHINE study
Abstract
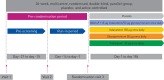
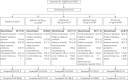
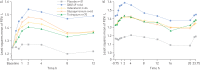
We investigated the efficacy and safety of dual bronchodilation with QVA149 versus its monocomponents indacaterol and glycopyrronium, tiotropium and placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This was a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, 26-week trial. Patients (n = 2144) were randomised (2:2:2:2:1) to receive once-daily QVA149 (indacaterol 110 μg/glycopyrronium 50 μg), indacaterol 150 μg, glycopyrronium 50 μg, open-label tiotropium 18 μg or placebo. The primary end-point was trough forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) at week 26 for QVA149 versus its monocomponents. Secondary end-points included dyspnoea, health status, rescue medication use and safety. Trough FEV1 at week 26 was significantly improved (p<0.001) with QVA149 compared with indacaterol and glycopyrronium (least squares mean (LSM) differences 0.07 L and 0.09 L, respectively), tiotropium and placebo (LSM differences 0.08 L and 0.20 L, respectively); these beneficial effects were sustained throughout the 26-week study. QVA149 significantly improved dyspnoea and health status versus placebo (p<0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively) and tiotropium (p = 0.007 and p = 0.009, respectively) at week 26. All treatments were well tolerated. Dual bronchodilation with once-daily QVA149 demonstrated superior and clinically meaningful outcomes versus placebo and superiority versus treatment with a single bronchodilator, with a safety and tolerability profile similar to placebo, supporting the concept of fixed-dose long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist combinations for the treatment of COPD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside the online version of this article at
Figures

Comment in
-
Bronchodilator combinations for COPD: real hopes or a new Pandora's box?Eur Respir J. 2013 Dec;42(6):1441-5. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00168313. Eur Respir J. 2013. PMID: 24293415 No abstract available.
-
Lack of clinically relevant differences between combination therapy and monotherapy in COPD.Eur Respir J. 2014 Apr;43(4):1204. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00143513. Eur Respir J. 2014. PMID: 24687670 No abstract available.
-
Lack of clinically relevant differences between combination therapy and monotherapy in COPD.Eur Respir J. 2014 Apr;43(4):1204-5. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00156313. Eur Respir J. 2014. PMID: 24687671 No abstract available.
References
-
- Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2013. www.goldcopd.org/guidelines-global-strategy-for-diagnosis-management.html Date last accessed: February 11, 2013. Date last updated: February 2013 - PubMed
-
- Vogelmeier C, Kardos P, Harari S, et al. Formoterol mono- and combination therapy with tiotropium in patients with COPD: a 6-month study. Respir Med 2008; 102: 1511–1520 - PubMed
-
- van Noord JA, Aumann JL, Janssens E, et al. Combining tiotropium and salmeterol in COPD: effects on airflow obstruction and symptoms. Respir Med 2010; 104: 995–1004 - PubMed
-
- Tashkin DP, Donohue JF, Mahler DA, et al. Effects of arformoterol twice daily, tiotropium once daily, and their combination in patients with COPD. Respir Med 2009; 103: 516–524 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
