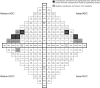
Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap)
- PMID: 23723294
- PMCID: PMC3755331
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt205
Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap)
Abstract
Background: Meta-analyses were conducted to characterize patterns of mutation incidence in non small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Design: Nine genes with the most complete published mutation coincidence data were evaluated. One meta-analysis generated a 'mutMap' to visually represent mutation coincidence by ethnicity (Western/Asian) and histology (adenocarcinoma [ADC] or squamous cell carcinoma). Another meta-analysis evaluated incidence of individual mutations. Extended analyses explored incidence of EGFR and KRAS mutations by ethnicity, histology, and smoking status.
Results: Genes evaluated were TP53, EGFR, KRAS, LKB1, EML4-ALK, PTEN, BRAF, PIK3CA, and ErbB2. The mutMap highlighted mutation coincidences occurring in ≥5% of patients, including TP53 with KRAS or EGFR mutations in patients with ADC, and TP53 with LKB1 mutation in Western patients. TP53 was the most frequently mutated gene overall. Frequencies of TP53, EGFR, KRAS, LKB1, PTEN, and BRAF mutations were influenced by histology and/or ethnicity. Although EGFR mutations were most frequent in patients with ADC and never/light smokers from Asia, and KRAS mutations were most frequent in patients with ADC and ever/heavy smokers from Western countries, both were detected outside these subgroups.
Conclusions: Potential molecular pathology segments of NSCLC were identified. Further studies of mutations in NSCLC are warranted to facilitate more specific diagnoses and guide treatment.
Keywords: geography; histology; lung cancer; mutation coincidence; oncogenes.
Figures
References
-
- Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Baade PD. The International Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:819–831. - PubMed
-
- Rodenhuis S, van de Wetering ML, Mooi WJ, et al. Mutational activation of the K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:929–935. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous