Domestic violence and perinatal mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23723741
- PMCID: PMC3665851
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001452
Domestic violence and perinatal mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Domestic violence in the perinatal period is associated with adverse obstetric outcomes, but evidence is limited on its association with perinatal mental disorders. We aimed to estimate the prevalence and odds of having experienced domestic violence among women with antenatal and postnatal mental disorders (depression and anxiety disorders including post-traumatic stress disorder [PTSD], eating disorders, and psychoses).
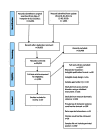
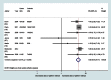
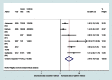
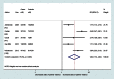
Methods and findings: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis (PROSPERO reference CRD42012002048). Data sources included searches of electronic databases (to 15 February 2013), hand searches, citation tracking, update of a review on victimisation and mental disorder, and expert recommendations. Included studies were peer-reviewed experimental or observational studies that reported on women aged 16 y or older, that assessed the prevalence and/or odds of having experienced domestic violence, and that assessed symptoms of perinatal mental disorder using a validated instrument. Two reviewers screened 1,125 full-text papers, extracted data, and independently appraised study quality. Odds ratios were pooled using meta-analysis. Sixty-seven papers were included. Pooled estimates from longitudinal studies suggest a 3-fold increase in the odds of high levels of depressive symptoms in the postnatal period after having experienced partner violence during pregnancy (odds ratio 3.1, 95% CI 2.7-3.6). Increased odds of having experienced domestic violence among women with high levels of depressive, anxiety, and PTSD symptoms in the antenatal and postnatal periods were consistently reported in cross-sectional studies. No studies were identified on eating disorders or puerperal psychosis. Analyses were limited because of study heterogeneity and lack of data on baseline symptoms, preventing clear findings on causal directionality.
Conclusions: High levels of symptoms of perinatal depression, anxiety, and PTSD are significantly associated with having experienced domestic violence. High-quality evidence is now needed on how maternity and mental health services should address domestic violence and improve health outcomes for women and their infants in the perinatal period.
Conflict of interest statement
LMH and GF are members of the WHO Guideline Development Group on Policy and Practice Guidelines for responding to Violence Against Women and the NICE/SCIE Guideline Development Group on Preventing and Reducing Domestic Violence. LMH has also been appointed as chair of the NICE guideline update on antenatal and postnatal mental health. The other authors declare no completing interests exist.
Figures


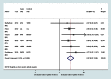

References
-
- Howard LM (2005) Fertility and pregnancy in women with psychotic disorders. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 119: 3–10. - PubMed
-
- Micali N, Simonoff E, Treasure J (2007) Risk of major adverse perinatal outcomes in women with eating disorders. Br J Psychiatry 190: 255–259. - PubMed
-
- Howard LM, Kirkwood G, Latinovic R (2007) Sudden infant death syndrome and maternal depression. J Clin Psychiatry 68: 1279–1283. - PubMed
-
- Webb R, Abel K, Pickles A, Appelby L (2005) Mortality in offspring of parents with psychotic disorders: a critical review and meta-analysis. Am J Psych 162: 1045–1056. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

