Thrombocytopenia in Plasmodium vivax malaria is related to platelets phagocytosis
- PMID: 23723981
- PMCID: PMC3665752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063410
Thrombocytopenia in Plasmodium vivax malaria is related to platelets phagocytosis
Abstract
Background: Although thrombocytopenia is a hematological disorder commonly reported in malarial patients, its mechanisms are still poorly understood, with only a few studies focusing on the role of platelets phagocytosis.
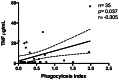
Methods and findings: Thirty-five malaria vivax patients and eight healthy volunteers (HV) were enrolled in the study. Among vivax malaria patients, thrombocytopenia (<150,000 platelets/µL) was found in 62.9% (22/35). Mean platelet volume (MPV) was higher in thrombocytopenic patients as compared to non-thrombocytopenic patients (p = 0.017) and a negative correlation was found between platelet count and MPV (r = -0.483; p = 0.003). Platelets from HV or patients were labeled with 5-chloromethyl fluorescein diacetate (CMFDA), incubated with human monocytic cell line (THP-1) and platelet phagocytosis index was analyzed by flow cytometry. The phagocytosis index was higher in thrombocytopenic patients compared to non-thrombocytopenic patients (p = 0.042) and HV (p = 0.048). A negative correlation was observed between platelet count and phagocytosis index (r = -0.402; p = 0.016). Platelet activation was assessed measuring the expression of P-selectin (CD62-P) in platelets' surface by flow cytometry. No significant difference was found in the expression of P-selectin between thrombocytopenic patients and HV (p = 0.092). After evaluating the cytokine profile (IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-17) in the patients' sera, levels of IL-6, IL-10 and IFN-γ were elevated in malaria patients compared to HV. Moreover, IL-6 and IL-10 values were higher in thrombocytopenic patients than non-thrombocytopenic ones (p = 0.044 and p = 0.017, respectively. In contrast, TNF-α levels were not different between the three groups, but a positive correlation was found between TNF-α and phagocytosis index (r = -0.305; p = 0.037).
Conclusion/significance: Collectively, our findings indicate that platelet phagocytosis may contribute to thrombocytopenia found in vivax malaria. Finally, we believe that this study opens new avenues to explore the mechanisms involved in platelet dysfunction, commonly found in vivax malaria patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization. (2011) World malaria report 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization. xii, 246 p. p.
-
- Anstey NM, Russell B, Yeo TW, Price RN (2009) The pathophysiology of vivax malaria. Trends Parasitol 25: 220–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

