Preliminary study on plasma RPN concentration of patients with infantile hemangioma treated with propranolol
- PMID: 23724152
- PMCID: PMC3664000
Preliminary study on plasma RPN concentration of patients with infantile hemangioma treated with propranolol
Abstract
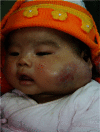
Propranolol (PRN) has recently been recommended as the first-line medicine for complicated infantile hemangiomas (IHs), because of the significant effect. However, no pharmacokinetic parameters have ever been reported for infants who receive PRN treatment for IH. In this study, we show that plasma PRN concentration is affected by the frequency of administration of PRN. A single daily administration of PRN (1 mg/kg/d) resulted in an early elevation of plasma PRN compared to a twice a day administration of the same dose. In contrast, the twice a day application resulted in a more prolonged expression at a later time-point. Our findings provide pharmacokinetic parameters of PRN action in IH for clinic.
Keywords: Infantile hemangioma; RP-HPLC; pharmacokinetics; propranolol.
Figures


References
-
- Amir J, Metzker A, Krikler R, Reisner SH. Strawberry hemangioma in preterm infants. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:331–332. - PubMed
-
- Finn MC, Glowacki J, Mulliken JB. Congenital vascular lesions: clinical application of a new classification. J Pediatr Surg. 1983;18:894–900. - PubMed
-
- Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW, Newell B, Nopper AJ, Frieden IJ. Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas: clinical characteristics predicting complications and treatment. Pediatrics. 2006;118:882–887. - PubMed
-
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB, Taïeb A. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2649–2651. - PubMed
-
- Holmes WJ, Mishra A, Gorst C, Liew SH. Propranolol as first-line treatment for rapidly proliferating Infantile Haemangiomas. JPRAS. 2011;64:445–451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
