MutS homologue hMSH4: interaction with eIF3f and a role in NHEJ-mediated DSB repair
- PMID: 23725059
- PMCID: PMC3689047
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-51
MutS homologue hMSH4: interaction with eIF3f and a role in NHEJ-mediated DSB repair
Abstract
Background: DNA mismatch repair proteins participate in diverse cellular functions including DNA damage response and repair. As a member of this protein family, the molecular mechanisms of hMSH4 in mitotic cells are poorly defined. It is known that hMSH4 is promiscuous, and among various interactions the hMSH4-hMSH5 interaction is involved in recognizing DNA intermediate structures arising from homologous recombination (HR).
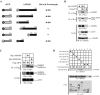
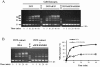
Results: We identified a new hMSH4 interacting protein eIF3f--a protein that functions not only in translation but also in the regulation of apoptosis and tumorigenesis in humans. Our studies have demonstrated that hMSH4-eIF3f interaction is mediated through the N-terminal regions of both proteins. The interaction with eIF3f fosters hMSH4 protein stabilization, which in turn sustains γ-H2AX foci and compromises cell survival in response to ionizing radiation (IR)-induced DNA damage. These effects can be, at least partially, attributed to the down-regulation of NHEJ activity by hMSH4. Furthermore, the interplay between hMSH4 and eIF3f inhibits IR-induced AKT activation, and hMSH4 promotes eIF3f-mediated bypass of S phase arrest, and ultimately enhancing an early G2/M arrest in response to IR treatment.
Conclusion: Our current study has revealed a role for hMSH4 in the maintenance of genomic stability by suppressing NHEJ-mediated DSB repair.
Figures

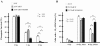



Similar articles
-
VBP1 facilitates proteasome and autophagy-mediated degradation of MutS homologue hMSH4.FASEB J. 2013 Dec;27(12):4799-810. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-235127. Epub 2013 Aug 20. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23964080 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage induced MutS homologue hMSH4 acetylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 18;14(10):20966-82. doi: 10.3390/ijms141020966. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24145748 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of hMSH4-hMSH5 heterocomplex is a prerequisite for subsequent GPS2 recruitment.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Jan 5;5(1):32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Aug 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16122992
-
MutS homologues hMSH4 and hMSH5: diverse functional implications in humans.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:905-11. doi: 10.2741/2112. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127347 Review.
-
Roles for 53BP1 in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102915. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087281 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Mismatch Repair Gene Variants in Sporadic Solid Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 3;21(15):5561. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155561. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32756484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Identification of Determinants for Single-Strand Annealing-Mediated Deletion Formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Oct 5;7(10):3269-3279. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300165. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28818866 Free PMC article.
-
VBP1 facilitates proteasome and autophagy-mediated degradation of MutS homologue hMSH4.FASEB J. 2013 Dec;27(12):4799-810. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-235127. Epub 2013 Aug 20. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23964080 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic inactivation of DNA repair genes as promising prognostic and predictive biomarkers in urothelial bladder carcinoma patients.Mol Genet Genomics. 2022 Nov;297(6):1671-1687. doi: 10.1007/s00438-022-01950-x. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Mol Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36076047 Free PMC article.
-
MutS homologue hMSH5: recombinational DSB repair and non-synonymous polymorphic variants.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 4;8(9):e73284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073284. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023853 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

