CD11a polymorphisms regulate TH2 cell homing and TH2-related disease
- PMID: 23726040
- PMCID: PMC3842370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.03.049
CD11a polymorphisms regulate TH2 cell homing and TH2-related disease
Abstract
Background: TH2-dependent diseases vary in severity according to genotype, but relevant gene polymorphisms remain largely unknown. The integrin CD11a is a critical determinant of allergic responses, and allelic variants of this gene might influence allergic phenotypes.
Objective: We sought to determine major CD11a allelic variants in mice and human subjects and their importance to allergic disease expression.
Methods: We sequenced mouse CD11a alleles from C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains to identify major polymorphisms; human CD11a single nucleotide polymorphisms were compared with allergic disease phenotypes as part of the international HapMap project. Mice on a BALB/c or C57BL/6 background and congenic for the other strain's CD11a allele were created to determine the importance of mouse CD11a polymorphisms in vivo and in vitro.
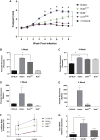
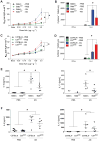
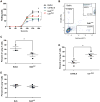
Results: Compared with the C57BL/6 allele, the BALB/c CD11a allele contained a nonsynonymous change from asparagine to aspartic acid within the metal ion binding domain. In general, the BALB/c CD11a allele enhanced and the C57BL/6 CD11a allele suppressed TH2 cell-dependent disease caused by the parasite Leishmania major and allergic lung disease caused by the fungus Aspergillus niger. Relative to the C57BL/6 CD11a allele, the BALB/c CD11a allele conferred both greater T-cell adhesion to CD54 in vitro and enhanced TH2 cell homing to lungs in vivo. We further identified a human CD11a polymorphism that significantly associated with atopic disease and relevant allergic indices.
Conclusions: Polymorphisms in CD11a critically influence TH2 cell homing and diverse TH2-dependent immunopathologic states in mice and potentially influence the expression of human allergic disease.
Keywords: AHR; Airway hyperreactivity; Asthma; CAMP; CD11a; Childhood Asthma Management Program; LD; LFA-1; Leukocyte function–associated antigen 1; Linkage disequilibrium; MIBD; Metal ion binding domain; OVA; Ovalbumin; PE; Phycoerythrin; Rag; Recombination-activating gene; SNP; Single nucleotide polymorphism; T(H)2 cell; WT; Wild-type; allele; allergic disease; biomarker; congenic; homing; polymorphism.
Copyright © 2013 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lee SH, Corry DB. Homing alone? CD18 in infectious and allergic disease. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:258–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Prince JE, Rais M, Kheradmand F, Shardonofsky F, Lu H, et al. Differential requirement for CD18 in T-helper effector homing. Nat Med. 2003;9:1281–6. - PubMed
-
- McDowall A, Leitinger B, Stanley P, Bates PA, Randi AM, Hogg N. The I domain of integrin leukocyte function-associated antigen-1 is involved in a conformational change leading to high affinity binding to ligand intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:27396–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

