53BP1 mediates productive and mutagenic DNA repair through distinct phosphoprotein interactions
- PMID: 23727112
- PMCID: PMC3713552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.023
53BP1 mediates productive and mutagenic DNA repair through distinct phosphoprotein interactions
Abstract
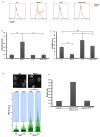
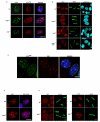
The DNA damage response (DDR) protein 53BP1 protects DNA ends from excessive resection in G1, and thereby favors repair by nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) as opposed to homologous recombination (HR). During S phase, BRCA1 antagonizes 53BP1 to promote HR. The pro-NHEJ and antirecombinase functions of 53BP1 are mediated in part by RIF1, the only known factor that requires 53BP1 phosphorylation for its recruitment to double-strand breaks (DSBs). Here, we show that a 53BP1 phosphomutant, 53BP18A, comprising alanine substitutions of the eight most N-terminal S/TQ phosphorylation sites, mimics 53BP1 deficiency by restoring genome stability in BRCA1-deficient cells yet behaves like wild-type 53BP1 with respect to immunoglobulin class switch recombination (CSR). 53BP18A recruits RIF1 but fails to recruit the DDR protein PTIP to DSBs, and disruption of PTIP phenocopies 53BP18A. We conclude that 53BP1 promotes productive CSR and suppresses mutagenic DNA repair through distinct phosphodependent interactions with RIF1 and PTIP.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
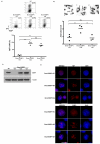
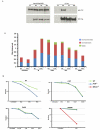
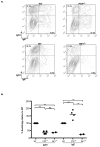
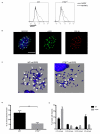

Comment in
-
DNA repair pathway choice--a PTIP of the hat to 53BP1.EMBO Rep. 2013 Aug;14(8):665-6. doi: 10.1038/embor.2013.99. Epub 2013 Jul 12. EMBO Rep. 2013. PMID: 23846307 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Ear US, Koller BH, Weichselbaum RR, Bishop DK. The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2000;275:23899–23903. - PubMed
-
- Boboila C, Jankovic M, Yan CT, Wang JH, Wesemann DR, Zhang T, Fazeli A, Feldman L, Nussenzweig A, Nussenzweig M, et al. Alternative end-joining catalyzes robust IgH locus deletions and translocations in the combined absence of ligase 4 and Ku70. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:3034–3039. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

