Rev-Erbs repress macrophage gene expression by inhibiting enhancer-directed transcription
- PMID: 23728303
- PMCID: PMC3839578
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12209
Rev-Erbs repress macrophage gene expression by inhibiting enhancer-directed transcription
Abstract
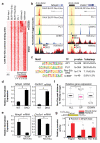
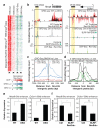
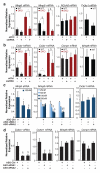
Rev-Erb-α and Rev-Erb-β are nuclear receptors that regulate the expression of genes involved in the control of circadian rhythm, metabolism and inflammatory responses. Rev-Erbs function as transcriptional repressors by recruiting nuclear receptor co-repressor (NCoR)-HDAC3 complexes to Rev-Erb response elements in enhancers and promoters of target genes, but the molecular basis for cell-specific programs of repression is not known. Here we present evidence that in mouse macrophages Rev-Erbs regulate target gene expression by inhibiting the functions of distal enhancers that are selected by macrophage-lineage-determining factors, thereby establishing a macrophage-specific program of repression. Remarkably, the repressive functions of Rev-Erbs are associated with their ability to inhibit the transcription of enhancer-derived RNAs (eRNAs). Furthermore, targeted degradation of eRNAs at two enhancers subject to negative regulation by Rev-Erbs resulted in reduced expression of nearby messenger RNAs, suggesting a direct role of these eRNAs in enhancer function. By precisely defining eRNA start sites using a modified form of global run-on sequencing that quantifies nascent 5' ends, we show that transfer of full enhancer activity to a target promoter requires both the sequences mediating transcription-factor binding and the specific sequences encoding the eRNA transcript. These studies provide evidence for a direct role of eRNAs in contributing to enhancer functions and suggest that Rev-Erbs act to suppress gene expression at a distance by repressing eRNA transcription.
Figures

Comment in
-
Enhancer-derived RNAs: 'spicing up' transcription programs.EMBO J. 2013 Jul 31;32(15):2096-8. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.151. Epub 2013 Jun 21. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23792424 Free PMC article.
-
eRNAs reach the heart of transcription.Cell Res. 2013 Oct;23(10):1151-2. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.97. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23877407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Preitner N, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadiantranscription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell. 2002;110(2):251–260. - PubMed
-
- Raspé E, et al. Identification of Rev-erbalpha as a physiological repressor of apoC-III gene transcription. J Lipid Res. 2002;43(12):2172–2179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK062434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA17390/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007198-37/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173903/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19DK62434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA52599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007198/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

