Thrombolysis (different doses, routes of administration and agents) for acute ischaemic stroke
- PMID: 23728633
- PMCID: PMC7045424
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000514.pub3
Thrombolysis (different doses, routes of administration and agents) for acute ischaemic stroke
Abstract
Background: Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability world wide. Thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is licensed for treatment of acute ischaemic stroke in the early hours after symptom onset. It has been shown in randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and the 2009 Cochrane review of thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke to reduce dependency but at the increased risk of intracranial haemorrhage. Methods to reduce the risk of haemorrhage while retaining or enhancing the benefit could increase the use of thrombolytic treatment. While most available information comes from RCTs of intravenous rt-PA at 0.9 mg/kg, it is possible that other doses, drugs and other routes of administration might increase benefit and reduce the hazard.
Objectives: To assess the risks and benefits of different thrombolytic agents, doses and routes of administration for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register (May 2012), MEDLINE (1966 to May 2012) and EMBASE (1980 to May 2012). We handsearched journals and conference proceedings, searched ongoing trials registers and contacted pharmaceutical companies and researchers.
Selection criteria: Unconfounded randomised and quasi-randomised trials of different doses of a thrombolytic agent, or different agents, or the same agent given by different routes, in people with confirmed acute ischaemic stroke.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial eligibility and quality, and extracted the data using a structured proforma. We cross-checked and resolved discrepancies by discussion to reach consensus. We obtained translations and additional information from study authors where required.
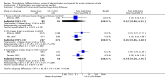
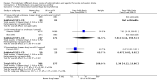
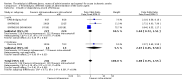
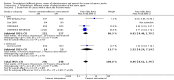
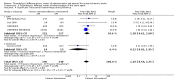
Main results: We included 20 trials involving 2527 patients. Concealment of allocation was poorly described. Different doses (of tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase, desmoteplase or tenecteplase) were compared in 13 trials (N = 1433 patients). Different agents (tissue plasminogen activator versus urokinase, tissue-cultured urokinase versus conventional urokinase, tenecteplase versus tissue plasminogen activator) were compared in five trials (N = 875 patients). Five trials (N = 485) compared different routes of administration. As some trials compared different agents and different doses, some patients contributed to two analyses. There was an approximately three-fold increase in fatal intracranial haemorrhages in patients allocated to higher than to lower doses of the same thrombolytic drug (odds ratio (OR) 2.71, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.22 to 6.04). There was no difference in the number of patients who were dead or dependent at the end of follow-up between those allocated higher or lower doses of thrombolytic drug (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.19). Higher versus lower doses of desmoteplase were associated with more deaths at the end of follow-up (OR 3.21, 95% CI 1.23 to 8.39). There was no evidence of any benefit for intra-arterial over intravenous treatment.
Authors' conclusions: These limited data suggest that higher doses of thrombolytic agents may lead to higher rates of bleeding. However, the evidence is inadequate to conclude whether lower doses of thrombolytic agents are more effective than higher doses, or whether one agent is better than another, or which route of administration is the best, for acute ischaemic stroke. At present, intravenous rt-PA at 0.9mg/kg as licensed in many countries appears to represent best practice and other drugs, doses or routes of administration should only be used in randomised controlled trials.
Conflict of interest statement
JMW (and other academic colleagues) was awarded grants to perform the Third International Stroke Trial, a multicentre international randomised controlled trial of rt‐PA versus control in acute ischaemic stroke. The funders included the UK Medical Research Council, the Emerging Medicines Evaluation initiative of the National Institutes of Health Research UK, the Stroke Association, and numerous other governmental and charitable funders. These grants were all administered by the University of Edinburgh and funded staff, equipment and consumables. I received no personal salary or other direct funding from any of these.
Many years ago, the University of Edinburgh established a Brain Research Imaging Centre Magnetic Resonance scanner with academic government grants and some collaborative support from industry. The Industry funders were the MR equipment manufacturer Elscint (now taken over by GE) who provided the majority industry investment, Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis, both of whom provided small contributions worth less than 5% of the total cost of the facility.
PK and ML have no known conflicts of interest.
Figures
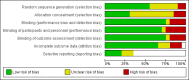
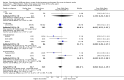






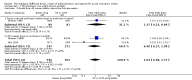
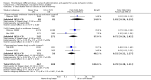



Update of
-
Thrombolysis (different doses, routes of administration and agents) for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD000514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000514.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;(5):CD000514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000514.pub3. PMID: 15494998 Updated.
Comment in
-
In patients with acute ischemic stroke, do different thrombolytic doses, agents, or routes of administration lead to different outcomes?Ann Emerg Med. 2014 Apr;63(4):435-6. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Ann Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 24199840 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abe 1981 {published data only}
-
- Abe T, Kazama M, Naito I, et al. Clinical effect of urokinase (60 000 units/day) on cerebral infarction ‐ comparative study by means of multiple center double blind test. Blood and Vessel 1981;12:342‐58.
Abe 1990 {published data only}
-
- Abe T, Terashi A, Tohgi H, et al. Clinical efficacy of intravenous administration of SM‐9527 (t‐PA) in cerebral thrombolysis ‐ multi‐centre double‐blind study in comparison with urokinase. Clinical Evaluation 1990;18:39‐69.
-
- Yamaguchi T, Hayakawa T, Kikuchi H, Abe T. Thrombolytic therapy in embolic and thrombotic cerebral infarction: a cooperative study. In: Hacke W, Zoppo GJ, Hirschberg M editor(s). Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke. 1st Edition. Berlin: Spinger‐Verlag, 1990:168‐9.
Atarashi 1985 {published data only}
-
- UK‐BR Study Group (Atarashi J, Ohtomo E, Araki G, Itoh E, Togi H, Matsuda T). Clinical utility of urokinase in the treatment of acute stage of cerebral thrombosis ‐ multi‐center double blind study in comparison with placebo. Clinical Evaluation 1985;13:659‐709.
Chen 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Chen Q, He M. Intravenous thrombolysis with urokinase for acute cerebral infarction. The study group of a 5 year National Project of the People's Republic of China. Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thrombolysis and Acute Stroke Therapy, 27‐28 May, Lyon, France. 2002.
-
- Chen Q‐T. Intravenous fibrinolytic therapy for acute ischaemic stroke. In preparation 2002.
DEDAS {published data only}
-
- Furlan AJ, Eyding D, Albers GW, Al‐Rawi Y, Lees KR, Rowley HA, et al. Dose Escalation of Desmoteplase for Acute ischemic Stroke (DEDAS): evidence of safety and efficacy 3 to 9 hours after stroke onset. Stroke 2006;37(5):1227‐31. - PubMed
DIAS‐2 {published data only}
-
- Fiebach JB, Al‐Rawi Y, Wintermark M, Furlan AJ, Hacke W, Rowley HA, et al. Vascular occlusion as imaging biomarker in selecting acute ischaemic stroke patients for treatment with desmoteplase. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011;31 Suppl 2:165.
-
- Forest Laboratories. Study of Desmoteplase (International Nonproprietary Name [INN]) in Acute Ischemic Stroke (DIAS‐2). ClinicalTrials.gov 2005.
-
- Hacke W, Furlan AJ, Al‐Rawi Y, Davalos A, Fiebach JB, Gruber F, et al. Intravenous desmoteplase in patients with acute ischaemic stroke selected by MRI perfusion‐diffusion weighted imaging or perfusion CT (DIAS‐2): a prospective, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Lancet Neurology 2009;8:141‐50. - PMC - PubMed
DIAS 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hacke W, Albers G, Al‐Rawi Y, Bogousslavsky J, Davalos A, Eliasziw M, et al. The Desmoteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke Trial (DIAS): a phase II MRI‐based 9‐hour window acute stroke thrombolysis trial with intravenous desmoteplase. Stroke 2005;36(1):66‐73. - PubMed
Ducrocq 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ducrocq X, Anxionnat R, Taillandier L, Lacour JC, Bracard S, Bollaert PE, et al. Intravenous versus intra‐arterial urokinase thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Randomised study of 27 patients. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2000;10(Suppl 2):76.
-
- Ducrocq X, Bracard S, Taillandier L, Anxionnat R, Lacour J‐C, Guillemin F, et al. Comparison of intravenous and intra‐arterial urokinase thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke: randomised study of 27 patients. Unpublished 2001. - PubMed
-
- Ducrocq X, Bracard S, Taillandier, Anxionnat R, Lacour JC, Guillemin F, et al. Comparison of intravenous and intra‐arterial urokinase thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Randomised study of 27 patients. Journal of Neuroradiology 2005;32:26‐32. - PubMed
EMS Bridging Trial {published data only}
-
- Emergency Management of Stroke (EMS) Investigators. Combined intraarterial and intravenous tPA for stroke (abstract). Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Stroke and Cerebral Circulation; San Antonio, Texas, USA. 1996.
-
- Lewandowski CA, Frankel M, Tomsick T, Broderick J, Frey J, Clark W, et al. Combined intravenous and intra‐arterial r‐TPA versus intra‐arterial therapy of acute ischaemic stroke. Emergency Management of Stroke (EMS) Bridging Trial. Stroke 1999;30:2598‐605. - PubMed
-
- The EMS Bridging Trial Investigators. Combined intravenous and intra‐arterial thrombolysis versus intra‐arterial thrombolysis alone: preliminary safety and clot lysis. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1996;6:184.
-
- The EMS Bridging Trial Investigators. Combined intravenous/intraarterial thrombolytic therapy: safety, time to treatment, and frequency of clot. Stroke 1996;27(1):2.
Kikuchi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kikuchi H, Yamaguchi T, Abe H, et al. Thrombolytic therapy of SM‐9527 (duteplase; rt‐PA) in hyperacute embolic stroke ‐ the clinical efficacy and safety of thrombolytic agent in a randomized double‐blind study. Clinical Evaluation 1994;22:105‐39.
-
- Yamaguchi T. Randomized dose comparison (20 and 30) million international unit of (t‐PA), double blind trial in stroke. Stroke 1994;25:253.
-
- Yamaguchi T, Kikuchi H, Hayakawa T for the Japanese Thrombolysis Study Group. Clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in acute embolic stroke: a randomised, double‐blind, dose‐comparison study of duteplase. In: Yamaguchi T, Mori E, Minematsu K, Zoppo GJ editor(s). Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke III. Tokyo: Springer‐Verlag, 1995.
Mori 1992 {published data only}
-
- Mori E, Yoneda Y, Tabuchi M, Yoshida T, Ohkawa S, Ohsumi Y, et al. Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in acute carotid artery territory stroke. Neurology 1992;42:976‐82. - PubMed
Ohtomo 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ohtomo E, Araki G, Itoh E, Toghi H, Matsuda T, Atarashi J. Clinical efficacy of urokinase in patients with cerebral thrombosis ‐ multicentre double blind study. Kiso‐to‐Rinshyo (Basic and Clinical) 1985;19:445‐78.
Ohtomo 1988a {published data only}
-
- Ohtomo E, et al. Clinical efficacy of AK‐124 (tissue plasminogen activator) in the treatment of cerebral thrombosis ‐ dose‐finding study by means of multi‐center double blind comparison. Yakuri to Chiryo (Pharmacology and Therapy) 1988;16(5):327‐53.
Ohtomo 1988b {published data only}
-
- Ohtomo E, et al. Clinical efficacy of AK ‐124 (tissue plasminogen activator) in the treatment of cerebral thrombosis ‐ study by means of multi‐center double blind comparison with urokinase. Pharmacology and Therapy 1988;16(9):167‐213.
Parsons 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Parsons M. Low‐dose tenecteplase versus standard‐dose alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: an imaging‐based efficacy trial. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ANZCTR) http://www.anzctr.org.au 2008.
-
- Parsons M, Spratt N, Bivard A, Campbell B, Chung K, Miteff F, et al. A randomised trial of tenecteplase versus alteplase for acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366:1099‐107. - PubMed
-
- Parsons MW, Bivard A, Campbell B, Chong KK, Miteff F, Blandin C, et al. Tenecteplase versus alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: an imaging based efficacy trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011;31 Suppl 2:86.
Sen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sen S, Huang DY, Akhaven O, Wilson S, Verro P, Solander S. IV vs IA TPA in acute ischemic stroke with CT angiographic evidence of major vessel occlusion: a feasibility study. Neurocritical Care 2009;11:76‐81. - PubMed
SYNTHESIS {published data only}
-
- Ciccone A, Boccardi E, Coppola C, Gatti A, Guccione A, Santilli I, et al. Thrombolytic therapy for acute ischaemic stroke: the SYNTHESIS trial. Proceedings of the European Stroke Conference 21‐24 May 2003, Valencia, Spain. 2003.
-
- Ciccone A, Valvassori L, Ponzio M, Ballabio E, Gasparotti R, Sessa M, et al. Intra‐arterial or intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke? The SYNTHESIS pilot trial. Journal of Neurointerventional Surgery 2010;2:74‐9. - PubMed
SYNTHESIS EXPANSION {published data only}
-
- Ciccone A. Intra‐arterial versus systemic thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke (SYNTHESIS EXP). ClinicalTrials.gov 2008.
-
- Ciccone A. SYNTHESIS. Local versus systemic thrombolysis for acute stroke. Personal communication 2003.
-
- Ciccone A, Caputo D, Casoni F, Zini A, Checcarelli N, Muscia F, et al. SYNTHESIS Expansion: an ongoing randomized controlled trial on endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Baseline characteristics of the first 100 patients. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2010;29 Suppl 2:121‐2.
-
- Ciccone A, Motto C, Sgoifo A, Daolio M, Nichelatti M, Valvassori L, et al. Synthesis expansion: an ongoing randomized controlled trial on fast track intra‐arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Data on the first 200 patients. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011;31 Suppl 2:134.
-
- Ciccone A, Valvassori L, Nichelatti M. SYNTHESIS Expansion: design of a nonprofit, pragmatic, randomized, controlled trial on the best fast‐track endovascular treatment vs. standard intravenous alteplase for acute ischemic stroke. International Journal of Stroke 2011;6:259‐65. - PubMed
TNK‐S2B {published data only}
Wang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wang SY, Wang XL, Zeng H, Zuo Y, Hu N, Li XY, et al. Early intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Critical Care Medicine 2003;15(9):542‐5. - PubMed
-
- Wang XL, Zeng H, Fan K, Wang KY, Zuo Y, Wang SY, et al. Clinical study on early intravenous thrombolysis with rt‐PA for acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Neurology 2006;39(10):678‐83.
-
- Zeng H, Wang X, Qi X, Wang H. Thrombolytic therapy using actilyse (rt‐PA) in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Emergency Medicine 2006;15(5):457‐9.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abciximab 2001 {published data only}
-
- Qureshi AI. Safety and efficacy in intra‐arterial reteplase and intravenous Abciximab in patients with acute ischemic stroke. http://www.strokecenter.org/trials/clinicalstudies/safety‐and‐efficacy‐o... 2006. - PubMed
Amaro 2007 {published data only}
-
- Amaro S, Obach V, Cervera Z, Urra X, Gomez‐Choco M, Planas AM, et al. Course of matrix metalloproteinase‐9 isoforms after the administration of uric acid in patients with acute stroke. Journal of Neurology 2009;256:651‐6. - PubMed
-
- Amaro S, Soy D, Obach V, Cervera A, Planas AM, Chamorro A. A pilot study of dual treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and uric acid in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007;38:2173‐5. - PubMed
ARTIS {published data only}
-
- Zinkstok SM, Vermeulen M, Stam J, Haan RJ, Roos YB. Antiplatelet therapy in combination with rt‐PA thrombolysis in ischemic stroke (ARTIS): rationale and design of a randomized controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2010;29:79‐81. - PubMed
Australian UK Trial {published data only}
-
- Macleod MR, Davis SM, Mitchell PJ, Gerraty RP, Fitt G, Hankey GJ, et al. Results of a multicentre, randomised controlled trial of intra‐arterial urokinase in the treatment of acute posterior circulation ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;20:12‐7. - PubMed
Brichta 2010 {published data only}
-
- Brichta J, Goldemund D, Kara T, Bar M, Reif M, Mikulik R. Optimized tPA dosing in correlation with artery status ‐ acute stroke study: preliminary results. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:189.
Bu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bu X, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Su S, Ping B. Study on treatment time window for intravenous thrombolysis of acute ischaemic stroke. Modern Diagnosis and Treatment (Xian dai zhen duan yu zhi liao) 1998;9(5):267‐9.
CARNEROS‐1 {unpublished data only}
-
- Begelman SM. Phase 2 proof‐of‐concept study of the safety and efficacy of alfimeprase to rapidly open arteries and restore brain function following a stroke. ClinicalTrials.gov.
Christoforidis 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Christoforidis G, Mohammed Y, Kontzialis M, Caragine L, Sivka A. Does the method for intra‐arterial TPA delivery affect reperfusion rate?. Stroke 2008;39:591 (Abst P88).
CLEAR‐ER {unpublished data only}
-
- Pancioli AM. The combined approach to lysis utilizing eptifibatide and rt‐PA in acute ischemic stroke ‐ enhanced regimen. Proceedings of the International Stroke Conference; 24‐26 February 2010. 2010.
-
- Pancioli AM. The combined approach to lysis utilizing eptifibatide and rt‐PA in acute ischemic stroke enhanced regimen (The CLEAR‐ER Stroke Trial): an ongoing phase IIb trial. Proceedings of the International Stroke Conference 2011; 8‐11 February 2011; USA, Los Angeles. 2011.
Davalos 2003 {published data only}
-
- Davalos A, Leira R, Pedraza S, Blanco J, Serena J, Silva Y, et al. The usefulness of clinical‐DWI mismatch in the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke with reperfusion therapies. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2003;16 Suppl 4:64.
Del Zoppo 1989 {unpublished data only}
-
- Del Zoppo GJ for the rt‐PA Acute Stroke Group. An open multicenter trial of rt‐PA in acute stroke (safety and efficacy): a progress report. Fibrinolysis 1990;4 Suppl 3:18 (Abst 47). - PubMed
-
- Zoppo GJ, Poeck K, Pessin MS, Furlan A, Zivin J, Kase C, et al. An open multicentre trial of rt‐PA in acute stroke: safety and efficacy. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1989;62(1):27.
Ding 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ding Y, Yin XG. Small‐dose aspirin plus lumbrokinase in improving neurological function of patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;10(6):60‐3.
Dong 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dong S, Wu C, Lu X, Wang J, Ma R, Wang H. Urokinase used for intra‐arterial and intravenous thrombolysis for acute cerebral infarction: a clinical comparison study. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research Advances in Cerebrovascular Disease; 13‐15 October 2003; China, Chengdu: 2003:179‐81. 2003.
Fan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fan C, Chen Q, Chang J. Antithrombosis enzyme vs dextran‐40 in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Henan Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2001;4(5):10‐1.
Gahn 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gahn G, Kunz A, Putz V, Becker U, Goldhagen T, Hahn G, et al. Recanalisation of middle cerebral artery occlusion after either t‐PA or t‐PA combined with abciximab. Stroke 2004;35(1):291.
Gao 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gao QL, Han QY, Li BS. Comparative observation of urokinase injected by carotid and peripheral vein treating brain infarction. Journal of Clinical Medicine (Lin chuang nei ke za zhi) 1994;11(2):38‐9.
Geng 1998 {published data only}
-
- Geng JG, Wang YK, Wang YM. A comparison of efficacy of alternative thrombolysis intra‐arterially by DSA with small dose of urokinase in the treatment of cerebral infarction. Journal of Apoplexy and Nervous Diseases 1998;15(4):242‐3.
Huang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Huang R, Fang Y, Su Z. Clinical report of 31 cases of acute cerebral infarction treated with snake venom Svate‐IV. Chinese Journal of Nervous & Mental Diseases 1996;22(6):378.
ICTUS‐L {published data only}
-
- Guluma KZ, Hemmen TM, Olsen SE, Rapp KS, Lyden PD. A trial of therapeutic hypothermia via endovascular approach in awake patients with acute ischemic stroke: methodology. Academic Emergency Medicine 2006;13(8):820‐7. - PubMed
IMS I & II {published data only}
-
- Broderick JP, Tomsick T, Palesch Y. Pooled analysis of the IMS I and IMS II trials. Stroke 2007;38(2):505.
-
- The IMS II Trial Investigators. The Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) II study. Stroke 2007;38:2127‐35. - PubMed
-
- The IMS Study Investigators. Combined intravenous and intra‐arterial recanalization for acute ischemic stroke: the Interventional Management of Stroke study. Stroke 2004;35:904‐12. - PubMed
IMS‐III {published data only}
-
- Broderick JP, Tomsick TA. The Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) III Trial: an ongoing phase III trial. Proceedings of the International Stroke Conference; 24‐26 February 2010. 2010.
-
- Broderick JP, Tomsick TA. The Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) III trial: an ongoing phase III trial. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:83‐4.
-
- Broderick JP, Tomsick TA. The Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) III trial: an ongoing phase III trial. Proceedings of the 20th European Stroke Conference 2011; 24‐27 May 2011; Germany, Hamburg. 2011.
-
- Sohn JA, Broderick JP, Spilker JA, Tomsick TA, Hill MD, Jauch EC, et al. Sedation practice patterns in acute stroke endovascular therapy: The IMS III Trial experience. Stroke 2011;42(3):e229‐30.
ITAIS‐II {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Liao X, Zhao X, Wang C, Liu L, Zhou Y, et al. Imaging‐based thrombolysis trial in acute ischemic stroke‐II (ITAIS‐II). International Journal of Stroke 2009;4:49‐53. - PubMed
Itoh 1998 {published data only}
-
- Itoh H, Yamatani K, Oshida N, Shioi M, Takaba M, Kamiyama H, et al. Clinical effects of sodium ozagrel and urokinase in patients with acute cerebral infarction in the territory of the internal carotid artery. Brain and Nerve/No To Shinkei 1998;50(2):147‐55. - PubMed
J‐ACT {published data only}
-
- Yamaguchi T, Mori E, Minematsu K, Nakagawara J, Hashi K, Saito I, et al. Alteplase at 0.6 mg/kg for acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours of onset: Japan Alteplase Clinical Trial (J‐ACT). Stroke 2006;37(7):1810‐5. - PubMed
J‐MARS 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nakagawara J, Minematsu K, Okada Y, Tanahashi N, Nagahiro S, Mori E, et al. Thrombolysis with 0.6 mg/kg intravenous alteplase for acute ischemic stroke in routine clinical practice: the Japan post‐Marketing Alteplase Registration Study (J‐MARS). Stroke 2010;41:1984‐9. - PubMed
Kim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kim OJ, Koo YH, Kim DG, Kim WC, Kim HS. Intra‐arterial tirofiban therapy in ischemic stroke [Abstract]. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14 Suppl 1:41.
Kim 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kim GM, Bang OY, Chung CS, Lee KH. Partial recanalization after intraarterial thrombolysis: angiographic consequences and clinical outcome. Stroke 2008;39(2):589‐90.
Konta 1996 {published data only}
-
- Konta Y, Aizu K, Fuziwara, Matsui T. Evaluation of intravenous urokinase, ozagrel sodium and low molecular dextran therapy in acute ischaemic stroke ‐ comparison of infusion methods of urokinase. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1996;6:187.
Lavallee 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lavallee PC, Mazighi M, Saint‐Maurice JP, Meseguer E, Abboud H, Klein IF, et al. Stent‐assisted endovascular thrombolysis versus intravenous thrombolysis in internal carotid artery dissection with tandem internal carotid and middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2007;38:2270‐4. - PubMed
Lee 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lee JH, Seo DC, Kim JS, Lee MC. Therapeutic efficacy of urokinase and heparin in acute ischaemic stroke. Stroke 1994;25:268.
Leker 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Leker RR. Study of aspirin and tPA in acute ischemic stroke. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Li 2000f {published data only}
-
- Li P, Yan LJ, Kang H. The control study on thrombolysis through artery and vein in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine 2000;20(3):166‐7.
Li 2003b {published data only}
-
- Li J, Peng Y, Yang F, Liu K, Du X, Huang C. Treatment of acute cerebral infarction with acupuncture therapy Tong‐nao‐huo‐luo during super‐acute phase and acute phase: clinical and experiment study. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research Advances in Cerebrovascular Disease; 13‐15 October 2003. 2003.
Li 2003e {published data only}
-
- Li JY, Peng YZ, Yang F, et al. Clinical observation on effect of tongnao huoluo acupuncture therapy in treating acute cerebral infarction at ultra‐early or acute stage. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine/Chung‐kuo Chung Hsi 2003;23(10):736‐9. - PubMed
Liu 1991a {published data only}
-
- Liu CX. Efficacy analysis of DUM infusion interventionally on 33 cases of cerebral thrombosis. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine 1991;11(6):303‐5.
Liu 2000b {published data only}
-
- Liu X, Zhan G, Zheng Z. The clinical efficacy and safety of thrombolytic therapy with urokinase in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2000;2(3):177‐9.
Luo 1997 {published data only}
-
- Luo HW, Geng J, Liu YH. Clinical analysis of treating 50 patients with cerebral infarction by drugs through carotid artery. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine (Zhongguo shi yong nei ke za zhi) 1997;17(6):376.
Lyden 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lyden P. Intravenous thrombolysis plus hypothermia for acute treatment of ischemic stroke. Stroke Trials Registry, Internet Stroke Center: www.strokecenter.org/trials/ 2003. - PMC - PubMed
Lyden 2003a {published data only}
-
- Haley EC. Pilot study of TNK‐TPA in acute ischemic stroke. CRISP Database (accessed 12 December 2002).
-
- Haley EC, Lyden PD, Johnston KC, Hemmen TM, the TNK in Stroke Investigators. A pilot dose‐escalation safety study of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005;36:607‐12. - PubMed
-
- Lyden P, on behalf of the TNK for Stroke Investigators. Pilot study of tenecteplase (TNK) in acute ischemic stroke: preliminary report. Stroke 2003;34:246.
Macleod 2005 {published data only}
-
- Macleod MR, Davis SM, Mitchell PJ, Gerraty RP, Fitt G, Hankey GJ, et al. Results of a multicentre, randomised controlled trial of intra‐arterial urokinase in the treatment of acute posterior circulation ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;20(1):12‐7. - PubMed
MELT {published data only}
-
- Ogawa A, Mori E, MinematsuK, Taki W, Takahashi A, Nemoto S, et al. Randomized trial of intraarterial infusion of urokinase within 6 hours of middle cerebral artery stroke. The Middle Cerebral Artery Embolism Local Fibrinolytic Intervention Trial (MELT) Japan. Stroke 2007;38:2633‐9. - PubMed
MITI‐IV {published data only}
-
- Thijs VN, Peeters A, Vosko M, Aichner F, Schellinger PD, Schneider D, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled, dose‐ranging clinical trial of intravenous microplasmin in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2009;40(12):3789‐95. - PubMed
Morris 2003 {published data only}
-
- Morris DC, Mitsias P, Silver B, Zhang L, Daley S, Lewandowski C, et al. Abciximab and rt‐PA in acute ischaemic stroke treatment. Proceedings of the 28th AHA International Stroke Conference; February 13‐15 2003; USA, Phoenix, Arizona: The American Stroke Association. Abstract CTP16. 2003.
Qiang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Qiang D. The dynamic study of stroke MRI in hyperacute stroke patients with thrombolysis. Hong Kong Medical Journal 2001;7(4):16.
Qureshi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Qureshi AI. Safety and efficacy of intra‐arterial reteplase and intravenous abciximab in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. www.strokecenter.org 2002. - PubMed
Qureshi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Qureshi AI, Harris‐Lane P, Kirmani JF, Janjua N, Divani AA, Mohammad YM, et al. Intra‐arterial reteplase and intravenous abciximab in patients with acute ischemic stroke: an open‐label, dose‐ranging, phase I study. Neurosurgery 2006;59:789‐97. - PubMed
ReoPro Retavase MRI {published data only}
-
- Patient Recruitment and Public Liaison Office. ReoPro Retavase Reperfusion of Stroke Safety Study ‐ Imaging Evaluation. www.strokecenter.org (Internet Stroke Center) 2002.
Riedel 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Riedel A. Phase II pilot study of pro‐urokinase (Saruplase) in acute stroke with angiographically‐proven occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Unpublished.
Sakamoto 1996 {published data only}
-
- Sakamoto T, Harimoto K, Inoue S, Konishi A. Clinical effects of urokinase and sodium ozagrel in patients with acute symptomatic lacunar infarction. Brain and Nerve/No To Shinkei 1996;48(9):805‐9. - PubMed
Seitz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Seitz RJ, Meisel S, Moll M, Wittsack H‐J, Junghans U, Siebler M. The effect of combined thrombolysis with rtPA and tirofiban on ischemic brain lesions. Neurology 2004;62:2110‐2. - PubMed
Song 2000 {published data only}
-
- Song JY, Zhang Y, Zhan JS, et al. A comparison of efficacy of carotid artery thrombolysis and venous thrombolysis with urokinase in acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine ‐ Zhongguo Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2000;12(5):287‐9.
Song 2003 {published data only}
-
- Song X, Xu G, Zhu R, Yu M, Wu X, Yu S, et al. Intracarotid thrombolysis in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research Advances in Cerebrovascular Disease; 13‐15 October 2003; China, Chengdu: 2003:171‐3. 2003.
TASS {published data only}
-
- Haley EC. Pilot study of TNK‐TPA in acute ischaemic stroke, treated within 3 hours. CRISP Database (electronic), also Internet Stroke Trials Directory www.strokecenter.org 2002.
-
- Lyden P, on behalf of the TNK for Stroke Investigators. Pilot study of tenecteplase (TNK) in acute ischaemic stroke: preliminary report. Stroke 2003;34:246.
Tazaki 1987 {published data only}
-
- Tazaki Y, Kobayashi S, Togi H, Ohtomo E, Goto F, Araki G, et al. Therapeutic effect of thrombin inhibitor MD‐805 in cerebral thrombosis ‐ double blinded comparative study with tissue cultured urokinase. Igaku no Ayumi 1987;141:499‐515.
TNK‐TPA {published data only}
-
- Molina CA, Ribo M, Rubiera M, Santamarina E, Delgado‐Mederos R, Maisterra O, et al. TNK induces faster MCA recanalization and leads to better short‐ and long‐term clinical outcomes than native tPA. The TNK‐TPA reperfusion stroke study. Stroke 2008;39(2):563.
Tsuchiya 1989 {published data only}
-
- Tsuchiya T, Fujikake K, Oku K. Effects of urokinase and heparin on hemorrhagic infarction, recanalization, recurrence ‐ analysis of 111 cases with middle cerebral artery occlusion on an acute stage in a prospective controlled trial. Japanese Journal of Stroke 1989;11:500‐10.
Tsuchiya 1990 {published data only}
-
- Tsuchiya T, Fujikake K, Oku K. A study on clinical effects of the combinated therapy of urokinase and heparin for acute lacunar infarcts in a prospective controlled trial. Japanese Journal of Stroke 1990;11:177‐84.
TTT‐AIS {published data only}
-
- Chao AC, Hsu HY, Chung CP, Liu CH, Chen CH, Teng MM, et al. Outcomes of thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke in Chinese patients: the Taiwan Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke (TTT‐AIS) study. Stroke 2010;41(5):885‐90. - PubMed
URICO‐ICTUS {published data only}
-
- Amaro S, Canovas D, Castellanos M, Gallego J, Marti‐Fabregas J, Segura T, et al. The URICO‐ICTUS study, a phase 3 study of combined treatment with uric acid and rtPA administered intravenously in acute ischaemic stroke patients within the first 4.5 hours of onset of symptoms. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5:325‐8. - PubMed
VASTT {published data only}
-
- Hill M, Demaerschalk B, Teal P, Pawsey S, Kwiatkowski K, Stratton G. VASTT ‐ the V10153 acute stroke thrombolysis trial. International Journal of Stroke 2008;3 Suppl 1:133.
Wang 1999a {published data only}
-
- Wang Y. Observations of effect of defibrase in treatment of 30 cases with acute cerebral thrombosis. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine ‐ Zhongguo Ji Jiu Yi Xue 1999;19(8):485.
Wang 2007h {published data only}
-
- Wang F, Yang H, Chu L‐Z, Hu Y‐C, Sui J‐M, Liu J. Combined intravenous and intra‐arterial infusion of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases 2007;4(4):160‐3.
Won 2010 {published data only}
-
- Won YD, Yoo DS, Park JW, Shin HE, Huh PW, Kim KT. Clinical significance of perfusion/diffusion mismatching in additional intraarterial thrombolytic therapy after full dose i.v.‐tPA administration. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:110.
Wu 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wu X. Urokinase therapy in acute ischaemic stroke. Proceedings of the 4th Chinese Stroke Conference, Chengdu, China. 1995:149‐50.
Xiao 2002 {published data only}
-
- Xiao KT, Xu KE. Observation of efficacy of intra‐arterial thrombolysis and intravenous thrombolysis in 54 cases with acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine ‐ Zhongguo Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2002;22(10):607.
Xu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Xu H‐Q, Shao B, Zhou C‐Y. Comparison of the curative effects between ahylsantinfarctase and defibrinogenase on cerebral infarction. Journal of Wenzhou Medical College 2000;30(2):124‐6.
Yan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Yan LJ, Ma R, Li P. Clinical study of thrombolysis with gene‐recombinant streptokinase on treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine (Zhongguo shi yong nei ke za zhi) 1997;17(11):667‐8.
Yoneda 1998 {published data only}
-
- Yoneda Y, Mori E, Uehara T, Tabuchi M. Intracarotid regional infusion of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1998;8:357‐9. - PubMed
Zhang 2001e {published data only}
-
- Zhang HX, Gu JQ, Han B. A study on alternative thrombolysis intra‐arterially in the treatment of cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine (Zhongguo shi yong nei ke za zhi) 2001;21(11):656‐7.
Zhang 2006c {published data only}
-
- Zhang XY, Li XG, Fan DS, Wang LP, Zhang Y, Sun AP, et al. Combined intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt‐PA) and free radical scavenger (edaravone) for acute ischemic stroke. International Journal of Stroke 2006;1 Suppl 1:146.
Zhou 1996b {published data only}
-
- Zhou Y, Gao H, Ma R. Functions changes of VEC and therapeutic effect on VEC in patients with acute cerebral infarct. Stroke and Nervous Diseases 1996;3(4):191‐3.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Wadia 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Wadia RS. Clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of TNK‐TPA in acute ischemic stroke. Clinical Trials Registry ‐ India (CTRI) http://www.ctri.in 2009.
References to ongoing studies
BASICS {unpublished data only}
-
- BASICS. Ongoing study To be confirmed.
DIAS‐J {published data only}
-
- Lundbeck Japan KK. Clinical study of desmoteplase in Japanese patients with acute ischemic stroke (DIAS‐J). ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
-
- Mori E. Desmoteplase in Japanese patients with acute ischaemic stroke (DIAS‐J): study objectives of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose escalation trial. International Journal of Stroke 2010;5 Suppl 2:192.
-
- Penner R. Paion's partner Lundbeck initiates Japanese clinical phase II trial with desmoteplase in ischaemic stroke. http://www.paion.de/images/stories/investoren/finanznachrichten/2010/en/... 2010.
-
- Kummer R, Albers GW, on behalf of the DIAS Steering Committee. Desmoteplase in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: status updated on the DIAS clinical trial programme. Poster presented at the 2011 European Stroke Conference; May 24‐27, 2011; Hamburg, Germany 2011.
ENCHANTED {unpublished data only}
-
- Lindley R. ENCHANTED. Powerpoint presentation.
FRALYSE {published and unpublished data}
-
- Trouillas P, Nighoghossian N, Derex L, Adeleine P. FRALYSE, a randomised blind multicenter study comparing 0.9mg/kg for 60 minutes and 0.8mg/kg for 90 minutes in a 7 hour window. Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thrombolysis and Acute Stroke Therapy; 27‐28 May 2002; Lyon, France. 2002:74.
ITAIS {published data only}
-
- Wang Y. ITAIS. Imaging‐based thrombolysis trial in acute ischemic stroke. Internet Stroke Center. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Jiang W, Liao X, Du B, Zhao X, Dong K, et al. Comparison of intravenous and intra‐arterial with tPA within 3‐6 hours guided by multi‐MRI: randomised study of 36 patients. Stroke 2008;39:602.
-
- Wang Y, Jiang W, Zhao X, Du B, Dong K, Liao X, et al. Imaging‐based thrombolysis trial in acute ischemic stroke. http://www.abstractsonline.com/arch/RecordPrintView.aspx?LookupKey=12345.... 2007. - PubMed
Additional references
APT 1994
Ciccone 2007
-
- Ciccone A, Valvassori L, Gasparotti R, Scomazzoni F, Ballabio E, Sterzi R. Debunking 7 myths that hamper the realization of randomized controlled trials on intra‐arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007;38:2191‐5. - PubMed
Galimanis 2012
-
- Galimanis A, Jung S, Mono ML, Fischer U, Findling O, Weck A, et al. Endovascular therapy of 623 patients with anterior circulation stroke. Stroke 2012;43:1052‐7. - PubMed
Hacke 2004
-
- Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, Kaste M, Kummer R, Broderick JP, et al. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt‐PA stroke trials. Lancet 2004;363:768‐74. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 5.1. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Lee 2010
-
- Lee M, Hong KS, Saver JL. Efficacy of intra‐arterial fibrinolysis for acute ischemic stroke: meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke 2010;41:932‐7. - PubMed
Lees 2010
-
- Lees KR, Bluhmki E, Kummer R, Brott TG, Toni D, Grotta JC, the ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS and EPITHET rt‐PA Study Group Investigators. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS and EPITHET trials. Lancet 2010;375:1695‐703. - PubMed
Lindsberg 2006
-
- Lindsberg PJ, Mattle HP. Therapy of basilar artery occlusion: a systematic analysis comparing intra‐arterial and intravenous thrombolysis. Stroke 2006;37:922‐8. - PubMed
Lisboa 2002
-
- Lisboa RC, Jovanovic BD, Alberts MJ. Analysis of the safety and efficacy of intraarterial thrombolytic therapy in ischaemic stroke. Stroke 2002;33:2866‐71. - PubMed
RECANALISE 2009
-
- Mazighi M, Serfaty JM, Labreuche J, Laissy JP, Meseguer E, Lavallée PC, et al. Comparison of intravenous alteplase with a combined intravenous‐endovascular approach in patients with stroke and confirmed arterial occlusion (RECANALISE study): a prospective cohort study. Lancet 2010;8:802‐9. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Tsivgoulis 2010
-
- Tsivgoulis G, Eggers J, Ribo M, Perren F, Saqqur M, Rubiera M, et al. Safety and efficacy of ultrasound‐enhanced thrombolysis: a comprehensive review and meta‐analysis of randomized and nonrandomized studies. Stroke 2010;41:280‐7. - PubMed
Wardlaw 2009
Wardlaw 2010
-
- Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, delZoppo GJ. Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2010;41:e445‐6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

