Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23728649
- PMCID: PMC10771320
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004525.pub2
Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Etanercept is a soluble tumour necrosis factor alpha-receptor disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objectives: The purpose of this review was to update the previous Cochrane systematic review published in 2003 assessing the benefits and harms of etanercept for the treatment of RA. In addition, we also evaluated the benefits and harms of etanercept plus DMARD compared with DMARD monotherapy in those people with RA who are partial responders to methotrexate (MTX) or any other traditional DMARD.
Search methods: Five electronic databases were searched from 1966 to February 2003 with no language restriction. The search was updated to January 2012. Attempts were made to identify other studies by contact with experts, searching reference lists and searching trial registers.
Selection criteria: All controlled trials (minimum 24 weeks' duration) comparing four possible combinations: 1) etanercept (10 mg or 25 mg twice weekly) plus a traditional DMARD (either MTX or sulphasalazine) versus a DMARD, 2) etanercept plus DMARD versus etanercept alone, 3) etanercept alone versus a DMARD or 4) etanercept versus placebo.
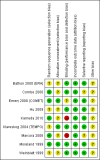
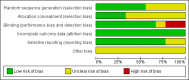
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed the risk of bias of the trials.
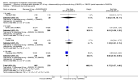
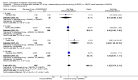
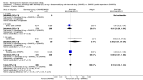
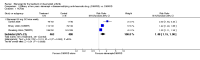
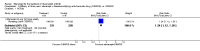
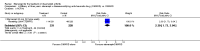
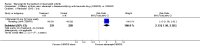
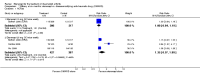
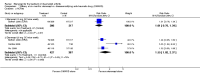
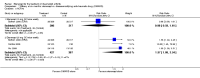
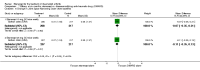
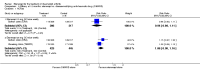
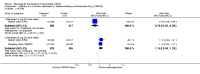
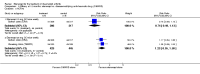
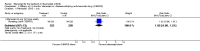
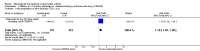
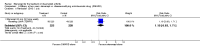
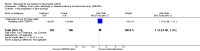
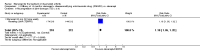
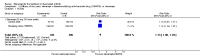
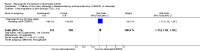
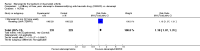
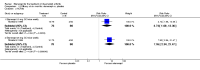
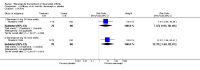
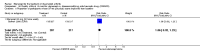
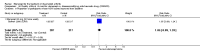
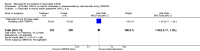
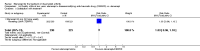
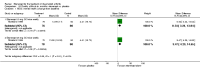
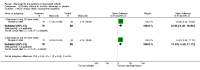
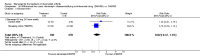
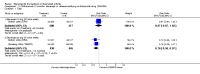
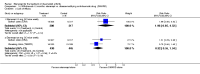
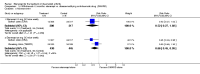
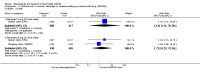
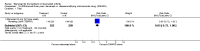
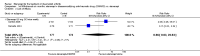
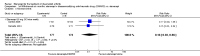
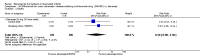
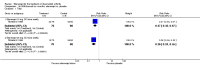
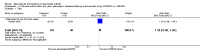
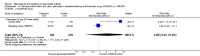
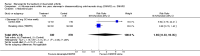
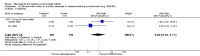
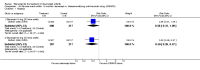
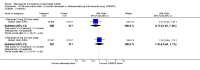
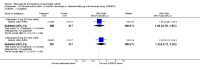
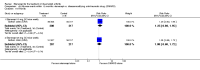
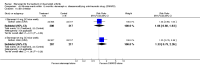
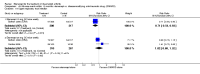
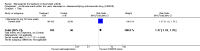
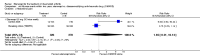
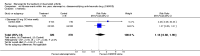
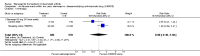
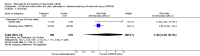
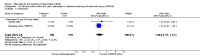
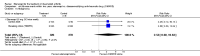
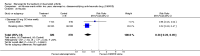
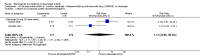
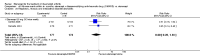
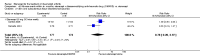
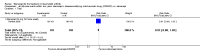
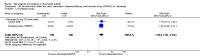
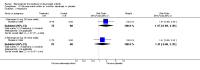
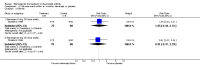
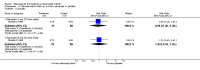
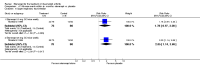
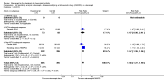
Main results: Three trials were included in the original version of the review. An additional six trials, giving a total of 2842 participants, were added to the 2012 update of the review. The trials were generally of moderate to low risk of bias, the majority funded by pharmaceutical companies. Follow-up ranged from six months to 36 months.BenefitAt six to 36 months the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50 response rate was statistically significantly improved with etanercept plus DMARD treatment when compared with a DMARD in those people who had an inadequate response to any traditional DMARD (risk ratio (RR) 2.0; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3 to 2.9, absolute treatment benefit (ATB) 38%; 95% CI 13% to 59%) and in those people who were partial responders to MTX (RR 11.7; 95% CI 1.7 to 82.5, ATB 36%). Similar results were observed when pooling data from all participants (responders or not) (ACR 50 response rates at 24 months: RR 1.9; 95% CI 1.3 to 2.8, ATB 29%; 36 months: RR 1.6; 95% CI 1.3 to 1.9, ATB 24%). Statistically significant improvement in physical function and a higher proportion of disease remission were observed in combination-treated participants compared with DMARDs alone ((mean difference (MD) -0.36; 95% CI -0.43 to -0.28 in a 0-3 scale) and (RR 1.92; 95% CI 1.60 to 2.31), respectively) in those people who had an inadequate response to any traditional DMARD. All changes in radiographic scores were statistically significantly less with combination treatment (etanercept plus DMARD) compared with MTX alone for all participants (responders or not) (Total Sharp Score (TSS) (scale = 0 to 448): MD -2.2, 95% CI -3.0 to -1.4; Erosion Score (ES) (scale = 0 to 280): MD -1.6; 95% CI -2.4 to -0.9; Joint Space Narrowing Score (JSNS) (scale = 0 to 168): MD -0.7; 95% CI -1.1 to -0.2), and with combination treatment compared with etanercept alone (TSS: MD -1.1; 95% CI -1.8 to -0.5; ES: MD -0.7; 95% CI -1.1 to -0.2; JSNS: MD -0.5, 95% CI -0.7 to -0.2). The estimate of irreversible physical disability over 10 years given the radiographic findings was 0.45 out of 3.0.When etanercept monotherapy was compared with DMARD monotherapy, there was generally no evidence of a difference in ACR50 response rates when etanercept 10 mg or 25 mg was used; at six months etanercept 25 mg was significantly more likely to achieve ACR50 than DMARD monotherapy but this difference was not found at 12, 24 or 36 months. TSS and ES radiographic scores were statistically significantly improved with etanercept 25 mg monotherapy compared with DMARD (TSS: MD -0.7; 95% CI -1.4 to 0.1; ES: MD -0.7; 95% CI -1.0 to -0.3) but there was no evidence of a statistically significant difference between etanercept 10 mg monotherapy and MTX.HarmsThere was no evidence of statistically significant differences in infections or serious infections between etanercept plus DMARD and DMARD alone at any point in time. Infection rates were higher in people receiving etanercept monotherapy compared with DMARD; however, there were no differences regarding serious infections. For those participants who had an inadequate response to DMARDs, the rate of total withdrawals was lower for the etanercept plus DMARD group compared with DMARD alone (RR 0.53; 95% CI 0.36 to 0.77, ATB 18%). No other statistically significant differences were observed in any of the assessed comparisons.
Authors' conclusions: Etanercept 25 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly together with MTX was more efficacious than either etanercept or MTX monotherapy for ACR50 and it slowed joint radiographic progression after up to three years of treatment for all participants (responders or not). There was no evidence of a difference in the rates of infections between groups.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
























































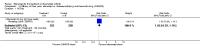
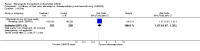
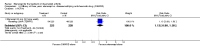





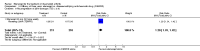













































































































































































































































































































Update of
-
Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD004525. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004525. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;(5):CD004525. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004525.pub2. PMID: 14584021 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bathon 2000 (ERA) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, et al. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;343:1586‐93. - PubMed
-
- Kosinski M, Kujawski SC, Martin R, Wanke LA, Buatti MC, Ware JE, et al. Health‐related quality of life in early rheumatoid arthritis: impact of disease and treatment response. The American Journal of Managed Care 2002;8(3):231‐40. - PubMed
Combe 2006 {published data only}
-
- Combe B, Codreanu C, Fiocco U, Gaubitz M, Geusens PP, Kvien TK, et al. Efficacy, safety and patient‐reported outcomes of combination etanercept and sulphasalazine versus etanercept alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a double‐blind randomised 2‐year study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2009;68(7):1146‐52. [PUBMED: 18794178] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Combe B, Codreanu C, Fiocco U, Gaubitz M, Geusens PP, Kvien TK, et al. Etanercept European Investigators Network (Etanercept Study 309 Investigators). Etanercept and sulphasalazine, alone and combined, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite receiving sulphasalazine: a double‐blind comparison. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2006;65(10):1357‐62. [PUBMED: 16606651] - PMC - PubMed
Emery 2008 (COMET) {published data only}
-
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, et al. Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double‐blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 2008;372:375‐82. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Heijde D, Ferraccioli G, Dougados M, Robertson D, et al. Two‐year clinical and radiographic results with combination etanercept‐methotrexate therapy versus monotherapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;62(3):674‐82. - PubMed
-
- Kekow J, Moots RJ, Emery P, Durez P, Koenig A, Singh A, et al. Patient‐reported outcomes improve with etanercept plus methotrexate in active early rheumatoid arthritis and the improvement is strongly associated with remission: the COMET trial. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69:222‐5. - PubMed
Hu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hu D, Bao C, Chen S, Gu J, Li Z, Sun L, et al. A comparison study of a recombinant tumour necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein (rhTNFR:Fc) and methotrexate in treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis in China. Rheumatology International 2009;29:297‐303. - PubMed
Kameda 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kameda H, Ueki Y, Saito K, Nagaoka S, Hidaka T, Atsumi T, et al. Japan Biological Agent Study Integrated Consortium. Etanercept (ETN) with methotrexate (MTX) is better than ETN monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite MTX therapy: a randomised trial. Modern Rheumatology 2010;20(6):531‐8. [PUBMED: 20574649] - PubMed
Klareskog 2004 (TEMPO) {published data only}
-
- Klareskog L, Heijde D, Jager JP, Gough A, Kalden J, Malaise M, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double‐blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;363:675‐81. - PubMed
-
- Heijde D, Klareskog L, Landewe R, Bruyn GAW, Cantagrel A, Durez P, et al. Disease remission and sustained halting of radiographic progression with combination etanercept and methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;56(12):3928‐39. - PubMed
-
- Heijde D, Klareskog L, Rodriguez‐Valverde V, Codreanu C, Bolosiu H, Melo‐Gomes J, et al. Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;54(4):1063‐74. - PubMed
Marcora 2006 {published data only}
-
- Marcora SM, Chester KR, Mittal G, Lemmey AB, Maddison PJ. Randomized phase 2 trial of anti‐tumour necrosis factor therapy for cachexia in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;84:1463‐72. - PubMed
Moreland 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mathias SD, Colwell HH, Miller DP, Moreland LW, Buatti M, Wanke L. Health‐related quality of life and functional status of patients with rheumatoid arthritis randomly assigned to receive etanercept or placebo. Clinical Therapeutics 2000;22(1):128‐39. - PubMed
-
- Moreland LW, Schiff MH, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Fleischmann, Bulpitt KJ, et al. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomised, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1999;130:478‐86. - PubMed
Weinblatt 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumour necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;340:253‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ACP 2001 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Etanercept was more effective and safer than methotrexate in disease progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. ACP Journal club July/August 2001;135(1):22.
Angel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Angel K, Provan SA, Gulseth HL, Mowinckel P, Kvien TK, Atar D. Tumor necrosis factor‐alpha antagonists improve aortic stiffness in patients with inflammatory arthropathies: a controlled study. Hypertension 2010;55(2):333‐8. - PubMed
Anis 2009 {published data only}
-
- Anis A, Zhang W, Emery P, Sun H, Singh A, Freundlich B, et al. The effect of etanercept on work productivity in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis: results from the COMET study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48(10):1283‐9. - PubMed
Benucci 2011 {published data only}
-
- Benucci M, Saviola G, Baiardi P, Manfredi M, Sarzi‐Puttini P, Atzeni F. Efficacy and safety of leflunomide or methotrexate plus subcutaneous tumour necrosis factor‐alpha blocking agents in rheumatoid arthritis. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2011;24(1):269‐76. - PubMed
Blank 2009 {published data only}
-
- Blank N, Max R, Schiller M, Briem S, Lorenz HM. Safety of combination therapy with rituximab and etanercept for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48(4):440‐1. - PubMed
Bliddal 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bliddal H, Terslev L, Qvistgaard E, Konig M, Holm CC, Rogind H, et al. A randomised, controlled study of a single intra‐articular injection of etanercept or glucocorticosteroids in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2006;35(5):341‐5. [PUBMED: 17062431] - PubMed
Boesen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Boesen M, Boesen L, Jensen KE, Cimmino MA, Torp‐Pedersen S, Terslev L, et al. Clinical outcome and imaging changes after intraarticular (IA) application of etanercept or methylprednisolone in rheumatoid arthritis: magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound‐Doppler show no effect of IA injections in the wrist after 4 weeks. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(4):584‐91. [PUBMED: 18322991] - PubMed
Chen 2006 {published data only}
Cuomo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cuomo G, Molinaro G, Montagna G, Migliaresi S, Valentini G. A comparison between the Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Disease Activity Score (DAS28) as measure of response to treatment in patients undergoing different therapeutic regimens. Reumatismo 2006;58(1):22‐5. - PubMed
De Filippis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Filippis L, Caliri A, Anghelone S, Scibilia G, Lo Gullo R, Bagnato G. Improving outcomes in tumour necrosis factor a treatment: comparison of the efficacy of the tumour necrosis factor a blocking agents etanercept and infliximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Panminerva Medica 2006;48(2):129‐35. [PUBMED: 16953150] - PubMed
De Stefano 2010 {published data only}
-
- Stefano R, Frati E, Nargi F, Baldi C, Menza L, Hammoud M, et al. Comparison of combination therapies in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: leflunomide‐anti‐TNF‐alpha versus methotrexate‐anti‐TNF‐alpha. Clinical Rheumatology 2010;29(5):517‐24. [PUBMED: 20082236] - PubMed
Garnero 2002 {published data only}
-
- Garnero P, Gineyts E, Christgau S, Finck B, Delmas PD. Association of baseline levels of urinary glucosyl‐galactosyl‐pyridinoline and type II collagen C‐telopeptide with progression of joint destruction in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;46(1):21‐30. - PubMed
Genovese 2002 {published data only}
-
- Genovese MC, Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, et al. Etanercept versus methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Two‐year radiographic and clinical outcomes. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;46(6):1443‐50. - PubMed
Genovese 2004 {published data only}
-
- Genovese MC, Cohen S, Moreland L, Lium D, Robbins S, Newmark R, et al. Combination therapy with etanercept and anakinra in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have been treated unsuccessfully with methotrexate. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;50(5):1412‐9. [PUBMED: 15146410] - PubMed
Gerlag 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gerlag DM, Hollis S, Layton M, Vencovský J, Szekanecz Z, Braddock M, et al. Preclinical and clinical investigation of a CCR5 antagonist, AZD5672, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;62(11):3154‐60. [PUBMED: 20662070] - PubMed
Holman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Holman AJ, Ng E. Heart rate variability predicts anti‐tumour necrosis factor therapy response for inflammatory arthritis. Autonomic Neuroscience 2008;143(1‐2):58‐67. - PubMed
Iwamoto 2009 {published data only}
-
- Iwamoto N, Kawakami A, Fujikawa K, Aramaki T, Kawashiri SY, Tamai M, et al. Prediction of DAS28‐ESR remission at 6 months by baseline variables in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with etanercept in Japanese population. Modern Rheumatology 2009;19(5):488‐92. - PubMed
Johnsen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Johnsen AK, Schiff MH, Mease PJ, Moreland LW, Maier AL, Coblyn JS, et al. Comparison of 2 doses of etanercept (50 vs 100 mg) in active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised double blind study. Journal of Rheumatology 2006;33(4):659‐64. - PubMed
Kavanaugh 2008 {published data only}
Keystone 2004 {published data only}
-
- Keystone EC, Schiff MH, Kremer JM, Kafka S, Lovy M, DeVries T, et al. Once‐weekly administration of 50 mg etanercept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of a multicenter, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;50(2):353‐63. - PubMed
Keystone 2009 {published data only}
-
- Keystone E, Freundlich B, Schiff M, Li J, Hooper M. Patients with moderate rheumatoid arthritis (RA) achieve better disease activity states with etanercept treatment than patients with severe RA. Journal of Rheumatology 2009;36(3):522‐31. - PubMed
Koumakis 2009 {published data only}
-
- Koumakis E, Wipff J, Avouac J, Kahan A, Allanore Y. Severe refractory rheumatoid arthritis successfully treated with combination rituximab and anti‐tumour necrosis factor‐alpha‐blocking agents. Journal of Rheumatology 2009;36(9):2125‐6. - PubMed
Lan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lan JL, Chou SJ, Chen DY, Chen YH, Hsieh TY, Young M Jr. A comparative study of etanercept plus methotrexate and methotrexate alone in Taiwanese patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a 12‐week, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2004;103(8):618‐23. - PubMed
Lisbona 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lisbona MP, Maymo J, Perich J, Almirall M, Pérez‐García C, Carbonell J. Etanercept reduces synovitis as measured by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis after only 6 weeks. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(3):394‐7. - PubMed
-
- Lisbona MP, Maymó J, Perich J, Almirall M, Carbonell J. Rapid reduction in tenosynovitis of the wrist and fingers evaluated by MRI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with etanercept. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(6):1117‐22. [PUBMED: 20448287] - PubMed
Lukas 2009 {published data only}
Lukas 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lukas C, Heijde D, Fatenajad S, Landewé R. Repair of erosions occurs almost exclusively in damaged joints without swelling. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(5):851‐5. - PubMed
Lukina 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lukina GV. Double‐blind trial of the effectiveness of antibodies to interferon‐gamma and tumour necrosis factor‐alpha in rheumatoid arthritis (preliminary results). Terapevticheskii Arkhiv 2001;73(5):12‐5. - PubMed
Luzi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Luzi G, Laganà B, Salemi S, Rosa R. Are glucocorticoids a consistent risk factor for infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients under treatment with methotrexate and etanercept?. Clinica Terapeutica 2009;160(2):121‐3. - PubMed
Machado 2009 {published data only}
-
- Machado P, Santos A, Pereira C, Loureiro C, Silva J, Chieira C, et al. Increased prevalence of allergic sensitisation in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti‐TNFalpha. Bone Spine 2009;76(5):508‐13. - PubMed
Moreland 1997 {published data only}
-
- Moreland LW, Baumgartner SW, Schiff MH, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Weaver AL, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumour necrosis factor receptor (p75)‐Fc fusion protein. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(3):141‐7. - PubMed
Moreland 2001 {published data only}
-
- Moreland LW, Cohen SB, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Bulpitt K, Martin R, et al. Long‐term safety and efficacy of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 2001;28(6):1238‐44. - PubMed
Paleolog 1998 {published data only}
-
- Paleolog EM. Modulation of angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor by tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin‐1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1998;41(7):1258‐65. - PubMed
Roux 2011 {published data only}
-
- Roux CH, Breuil V, Valerio L, Amoretti N, Brocq O, Albert C, et al. Etanercept compared to intraarticular corticosteroid injection in rheumatoid arthritis: double‐blind, randomised pilot study. Journal of Rheumatology 2011;38(6):1009‐11. [PUBMED: 21406499] - PubMed
Saleem 2009 {published data only}
-
- Saleem B, Brown AK, Keen H, Nizam S, Freeston J, Karim Z, et al. Disease remission state in patients treated with the combination of tumour necrosis factor blockade and methotrexate or with disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs: a clinical and imaging comparative study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2009;60(7):1915‐22. - PubMed
Sennels 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sennels H, Sørensen S, Ostergaard M, Knudsen L, Hansen M, Skjødt H, et al. Circulating levels of osteopontin, osteoprotegerin, total soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor‐kappa B ligand, and high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis randomised to etanercept alone or in combination with methotrexate. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2008;37(4):241‐7. [PUBMED: 18612923] - PubMed
van Riel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Riel PLC, Taggart AJ, Sany J, Gaubitz M, Nab HW, Pedersen R, et al. Efficacy and safety of combination etanercept and methotrexate versus methotrexate alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to methotrexate: the ADORE study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2006;65(11):1478‐83. - PMC - PubMed
Weinblatt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Weinblatt M, Schiff M, Goldman A, Kremer J, Luggen M, Li T, Chen D, et al. Selective co stimulation modulation using abatacept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis while receiving etanercept: a randomised clinical trial. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2007;66(2):228‐34. [PUBMED: 16935912] - PMC - PubMed
Weinblatt 2008 {published data only}
-
- Weinblatt ME, Schiff MH, Ruderman EM, Bingham CO, Li J, Louie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of etanercept 50mg twice a week in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had a sub‐optimal response to etanercept 50mg once a week. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;58(7):1921‐30. - PubMed
Weisman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Weisman MH, Paulus HE, Burch FX, Kivitz AJ, Fierer J, Dunn M, et al. A placebo‐controlled, randomised, double‐blinded study evaluating the safety of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and concomitant comorbid diseases. Rheumatology 2007;46(7):1122‐5. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
EMPIRE 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- EMPIRE (Etanercept and Methotrexate in Patients to Induce Remission in Early arthritis). Ongoing study October 2006.
France 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- An Open‐Label, Randomised Study to Evaluate the Radiographic Efficacy and Safety of Enbrel (Etanercept) Added to Methotrexate in Comparison with Usual Treatment in Subjects with Moderate Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity. Ongoing study June 2008.
Japanese 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- A Randomised, Double‐Blind, Multi‐Centre, Comparative Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Etanercept and Methotrexate in Japanese Subjects with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ongoing study June 2006.
Jobanputra 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Remission Induction in Very Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: a Comparison of Etanercept plus Methotrexate plus Steroid with Standard Therapy. Ongoing study December 2005.
Takeuchi 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Etanercept on Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy in Japan. Ongoing study June 2005.
Additional references
Arnett 1988
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31:315‐24. - PubMed
Boers 1994
-
- Boers M, Tugwell P, Felson DT. World Health Organization and International League of Associations for Rheumatology core endpoints for symptom modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21:86‐9. - PubMed
Bykerk 2012
-
- Bykerk VP, Akhavan P, Hazlewood GS, Schieir O, Dooley A, Haraoui B, et al. Canadian Rheumatology Association recommendations for pharmacological management of rheumatoid arthritis with traditional and biologic disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs. Journal of Rheumatology 2012;39(8):1559‐82. - PubMed
Donahue 2008
-
- Donahue KE, Gartlehner G, Jonas DE, Lux LJ, Thieda P, Jonas BL, et al. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and harms of disease‐modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008;148:124‐34. - PubMed
Felson 1993
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith D, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1993;36:729‐40. - PubMed
Felson 1995
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith D, et al. American College of Rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38:727‐35. - PubMed
Fernandez‐Cruz 2008
-
- Fernández‐Cruz E, Alecsandru D, Rodríguez‐Sainz C. Introduction to biological drugs. Actas Dermo‐Sifiliograficas 2008;99 Suppl 4:2‐6. [PUBMED: 19080985] - PubMed
Furst 2007
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jarvis 1999
-
- Jarvis B, Faulds D. Etanercept: a review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 1999;57(6):945‐66. [PUBMED: 10400407] - PubMed
Kievit 2007
Klareskog 2006
-
- Klareskog L, Gaubitz M, Rodriguez‐Valverde V, Malaise M, Dougados M, Wajdula J. A long‐term, open‐label trial of the safety and efficacy of etanercept (Enbrel) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis not treated with disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2006;65:1578‐84. - PMC - PubMed
Kobelt 2005
Lopez‐Olivo 2012
-
- Lopez‐Olivo MA, Tayar JH, Martinez‐Lopez JA, Pollono EN, Cueto JP, Gonzales‐Crespo MR, et al. Risk of malignancies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic therapy ‐ a meta‐analysis. JAMA 2012;308(9):898‐908. - PubMed
Molenaar 2000
-
- Molenaar E, Heijde D, Boers M. Update on outcome assessment in rheumatic disorders. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2000;12:91‐8. - PubMed
Moreland 2006
-
- Moreland LW, Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Kremer JM, Martin RW, Schiff MH, et al. Etanercept treatment in adults with established rheumatoid arthritis: 7 years of clinical experience. Journal of Rheumatology 2006;33:854‐61. - PubMed
Murray 1997
-
- Murray KM, Dahl SL. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor receptor (p75) Fc fusion protein (TNFR:Fc) in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 1997;31(11):1335‐8. [PUBMED: 9391689] - PubMed
OMERACT 1993
-
- OMERACT. Conference on outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20:526‐91. - PubMed
Pincus 1993
-
- Pincus T, Callahan LF. What is the natural history of rheumatoid arthritis?. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 1993;19:123‐51. - PubMed
Pincus 1999
-
- Pincus T, Stein CM. ACR 20: clinical or statistical significance?. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1999;42(8):1572‐6. - PubMed
Puolakka 2005
-
- Puolakka K. Work Capacity and Productivity Costs in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Five‐Year Prospective Study [dissertation]. Available from: ethesis.helsinki.fi/julkaisut/laa/kliin/vk/puolakka2/workcapa.pdf (accessed 12 March 2013). Helsinki: Academic Dissertation University of Helsinki, 2005.
Saag 2008
-
- Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiy J, Finney C, Curtis JR, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of non‐biologic and biologic disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care and Research 2008;59(6):762‐84. - PubMed
Singh 2009
Singh 2011
Singh 2012
-
- Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care and Research (Hoboken) 2012;64(5):625‐39. - PMC - PubMed
Smolen 2010a
Smolen 2010b
Tugwell 2011
van der Heijde 2005a
van der Heijde 2005b
-
- Heijde D, Landewe R, Klareskog L, Rodriguez‐Valverde V, Settas L, Pedersen R, et al. Presentation and analysis of data on radiographic outcome in clinical trials. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2005;52(1):49‐60. - PubMed
Yazici 2008
-
- Yazici Y, Adler NM, Yazici H. Most tumour necrosis factor inhibitor trials in rheumatology are undeservedly called 'efficacy and safety' trials: a survey of power considerations. Rheumatology 2008;47(7):1054‐7. - PubMed
Yee 2003
-
- Yee CS, Filer A, Pace A, Douglas K, Situnayake D, Rowe IF, West Midlands Rheumatology Services and Training Committee. The prevalence of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the West Midlands fulfilling the BSR criteria for anti‐tumour necrosis factor therapy: an out‐patient study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42(7):856‐9. [PUBMED: 12730544] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

