Autoinflation for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion
- PMID: 23728660
- PMCID: PMC11357689
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006285.pub2
Autoinflation for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion
Abstract
Background: This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in The Cochrane Library in Issue 4, 2006.Otitis media with effusion (OME) or 'glue ear' is an accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, in the absence of acute inflammation or infection. It is the commonest cause of acquired hearing loss in childhood and the usual reason for insertion of 'grommets'. Potential treatments include decongestants, mucolytics, steroids, antihistamines and antibiotics. Autoinflation devices have been proposed as a simple mechanical means of improving 'glue ear'.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of autoinflation compared with no treatment in children and adults with otitis media with effusion.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders Group Trials Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); PubMed; EMBASE; CINAHL; Web of Science; BIOSIS Previews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts; ICTRP and additional sources for published and unpublished trials. The date of the most recent search was 12 April 2013.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials that compared any form of autoinflation to no autoinflation in individuals with 'glue ear'.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies for inclusion, assessed risk of bias and extracted data from included studies.
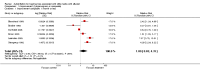
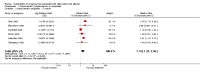
Main results: Eight studies, with a total of 702 participants, met the inclusion criteria. Overall, the studies were predominantly assessed as being at low or unclear risk of bias; unclear risk was mainly due lack of information. There was no evidence of selective reporting.Pooled estimates favoured the intervention, but did not show a significant effect on tympanometry (type C2 and B) at less than one month, nor at more than one month. Similarly, there were no significant changes for discrete pure-tone audiometry and non-discrete audiometry. Pooled estimates favoured, but not significantly, the intervention for the composite measure of tympanogram or audiometry at less than one month; at more than one month the result became significant (RRI 1.74, 95% CI 1.22 to 2.50). Subgroup analysis based on the type of intervention showed a significant effect using a Politzer device under one month (RRI 7.07, 95% CI 3.70 to 13.51) and over one month (RRI 2.25, 95% CI 1.67 to 3.04).None of the studies demonstrated a significant difference in the incidence of side effects between interventions.
Authors' conclusions: All of the studies were small, of limited treatment duration and had short follow-up. However, because of the low cost and absence of adverse effects it is reasonable to consider autoinflation whilst awaiting natural resolution of otitis media with effusion. Primary care could prove a beneficial place to evaluate such interventions and there is ongoing research in this area. Further research should also consider the duration of treatment, the long-term impact on developmental outcomes in children and additional quality of life outcome measures for children and families.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures









Update of
-
Autoinflation for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD006285. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006285. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;(5):CD006285. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006285.pub2. PMID: 17054290 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arick 2005 {published data only}
-
- Arick D, Silman S. Nonsurgical home treatment of middle ear effusion and associated hearing loss in children. Part I: Clinical trial. Ear, Nose and Throat Journal 2005;84(9):567‐78. - PubMed
Blanshard 1993 {published data only}
-
- Blanshard J, Maw A, Bawden R. Conservative treatment of otitis media with effusion by autoinflation of the middle ear. Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 1993;18:188‐92. - PubMed
-
- Blanshard J, Maw A, Bawden R. The treatment of otitis media with effusion in children by autoinflation. 2nd European Congress of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology and Cervico‐facial surgery. 1992:31‐7.
Brooker 1992 {published data only}
-
- Brooker D, McNeice A. Autoinflation in the treatment of glue ear in children. Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 1992;17:289‐90. - PubMed
De Nobili 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nobili E, Bellomo A. Comparative evaluation of efficacy of crenotherapeutic Politzer with sulphurous water versus crenotherapeutic Politzer and autoinflation (Otovent) in patients with tubaric dysfunction and secretory otitis media [Studio comparativo dell’efficacia del Politzer crenoterapico con acqua sulfurea versus Politzer crenoterapico e autoinsufflazione domiciliare (metodo Otovent®) in pazienti affetti da disfunzione tubarica e otite media secretiva]. Medicina Clinica e Termale 2008;20(64):30‐4.
Ercan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ercan I, Burak Ömür C, Kayaoglu S, Turgut S, Cerrahisi K, Kliniği Ş. Long term effect of autoinflation in the treatment of otitis media with effusion. KBB Forum 2005;4(4):166‐70.
Fraser 1977 {published data only}
-
- Fraser J, Mehta M, Fraser P. The medical treatment of secretory otitis media. A clinical trial of three commonly used regimes. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1977;91(9):757‐65. - PubMed
Lesinskas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lesinskas E. Factors affecting the results of non‐surgical treatment of secretory otitis media in adults. Auris, Nasus, Larynx 2003;30:7‐14. - PubMed
Stangerup 1992 {published data only}
-
- Stangerup S, Sederberg‐Olsen J, Balle V. Autoinflation as a treatment of secretory otitis media: a randomized controlled study. Archives of Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1992;118:149‐52. - PubMed
-
- Stangerup S, Tos M. Autoinflation in the treatment of Eustachian tube dysfunction, secretory otitis media and its sequelae. Recent Advances in Otitis Media. Amsterdam/New York: Kugler Publications, 1994:759‐63.
References to studies excluded from this review
Alper 1999 {published data only}
-
- Alper CM, Swarts JD, Doyle W. Middle ear inflation for diagnosis and treatment of otitis media with effusion. Auris Nasus Larynx 1999;26:479‐86. - PubMed
Arick 2000 {published data only}
-
- Arick D, Silman S. Treatment of otitis media with effusion based on politzerization with an automated device. Ear, Nose and Throat Journal 2000;79(4):290‐8. - PubMed
Blanshard 1995 {published data only}
-
- Blanshard J. Autoinflation for otitis media with effusion. Maternal and Child Health 1995;9:304‐7.
Chan 1989 {published data only}
-
- Chan K, Bluestone CD. Lack of efficacy of middle‐ear inflation: treatment of otitis media with effusion in children. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1989;100(4):317‐23. - PubMed
Costantino 2010 {published data only}
-
- Costantino M, Mastursi C, Contaldi E, Capua M, Filippelli A. The role of SPA therapy with Politzer method in dysfunction of the eustachian tube. Gazzetta Medica Italiana Archivio per le Scienze Mediche 2010;169(4):131‐6.
Dalchow 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dalchow C, Muenscher A, Knecht R. Endoscopic dilatation of the eustachian tube. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2011;145:93.
Ducla‐Soares 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ducla‐Soares JL, Santos‐Bento M, Laranjo S, Andrade A, Ducla‐Soares E, Boto JP, et al. Wavelet analysis of autonomic outflow of normal subjects on head‐up tilt, cold pressor test, Valsalva manoeuvre and deep breathing. Experimental Physiology 2007;92(4):677‐86. - PubMed
El Hachem 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hachem N, Halimi M. New technique for the passive opening of the Eustachian tube. Tympanometry assessment of the effect of a new manipulation technique on the opening of the Eustachian tube in children less than six years with otitis media with or without effusion [French]. Kinesitherapie 2012;132:25‐33.
Gottschalk 1966 {published data only}
-
- Gottschalk GH. Further experience with controlled middle ear inflation in the treatment of serous otitis. Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Monthly 1966;45:49‐51. - PubMed
Gottschalk 1991 {published data only}
-
- Gottschalk GH. Middle ear inflation: its place in the treatment of otitis media with effusion. In: Sadé J editor(s). The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases: Clinical Aspects. The Hague: Kugler Publications, 1991:293‐5.
Hanner 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hanner P. Non surgical treatment of otitis media with effusion. Indian Journal of Otology 1997;3(3):101‐7.
Havas 1995 {published data only}
-
- Havas T, Koutsis A, Jacobson I. Nasal balloon auto‐inflation (Otovent) as a treatment of otitis media with effusion in children. Journal of the Oto‐laryngological Society of Australia 1995;2(1):37‐41.
Hidir 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hidir Y, Ulus S, Karahatay S, Satar B. A comparative study on efficiency of middle ear pressure equalization techniques in healthy volunteers. Auris Nasus Larynx 2011;38(4):450‐5. - PubMed
Jumah 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jumah MD, Schlachta M, Hoelzl M, Werner A, Sedlmaier B. Pressure regulating ear plug testing in a pressure chamber. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine 2010;81(6):560‐5. - PubMed
Kaneko 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kaneko Y, Takasaka T, Sakuma M, Kambayashi J, Okitsu T. Middle ear inflation as a treatment for secretory otitis media in children. Acta Otolaryngologica (Stockholm) 1997;117:564‐8. - PubMed
Karahatay 2008 {published data only}
-
- Karahatay S, Yilmaz YF, Birkent H, Ay H, Satar B. Middle ear barotrauma with hyperbaric oxygen therapy: incidence and the predictive value of the nine‐step inflation/deflation test and otoscopy. Ear, Nose, and Throat Journal 2008;87(12):684‐8. - PubMed
Kawase 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kawase T, Hori Y, Kikuchi T, Oshima T, Kobayashi T. The effects of mastoid aeration on autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube. European Archives of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology 2008;265(8):893‐7. - PubMed
Kouwen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kouwen H, Balen FAM, Dejonckere PH. Functional tubal therapy for persistent otitis media with effusion in children: myth or evidence?. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 2005;69:943‐51. - PubMed
Kutácová 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kutácová S, Komínek P, Horník PS. Autoinflation in curing up the middle ear inflammation. Otorinolaryngologie a Foniatrie 2005;54(1):52‐5.
Laina 2006 {published data only}
-
- Laina V, Pothier DD. Should we aspirate middle‐ear effusions prior to insertion of ventilation tubes?. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2006;120(10):818‐21. - PubMed
Leach 2008 {published data only}
Leunig 1995 {published data only}
-
- Leunig A. Middle ear aeration with the Otovent‐latex membrane system. Laryno‐Rhino‐Otologie 1995;74(b):352‐4. - PubMed
Luntz 1991 {published data only}
-
- Luntz M, Sadé J. The diagnostic and therapeutic value of middle ear inflation. In: Sadé J editor(s). The Eustachian Tube, Basic Aspects. Amsterdam: Kugler and Ghedini, 1991:183‐5.
Ogawa 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ogawa I. Otitis media with effusion: treatment by autoinflation using a balloon. Journal of Otolaryngology of Japan 2003;106:685‐91. - PubMed
Pau 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pau HW, Sievert U, Just T, Sad J. Pressure changes in the human middle ear without opening the Eustachian tube. Acta Oto‐Laryngologica 2009;129(11):1182‐6. - PubMed
Poe 2011 {published data only}
-
- Poe DS, Silvola J, Pyykko I. Balloon dilation of the cartilaginous Eustachian tube. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2011;144(4):563‐9. - PubMed
Prabhakar 2007 {published data only}
-
- Prabhakar H, Bithal PK, Suri A, Rath GP, Dash HH. Intracranial pressure changes during Valsalva manoeuvre in patients undergoing a neuroendoscopic procedure. Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery 2007;50(2):98‐101. - PubMed
Shim 2010 {published data only}
Talmon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Talmon Y. In reference to an easy technique to prevent post‐tympanoplasty ventilation tube blockage. Laryngoscope 2010;120(6):1282. - PubMed
Toros 2010 {published data only}
-
- Toros SZ, Habesoglu TE, Habesoglu M, Bolukbasi S, Naiboglu B, Karaca CT, et al. Do patients with sclerotic mastoids require aeration to improve success of tympanoplasty?. Acta Oto‐Laryngologica 2010;130(8):909‐12. - PubMed
Yu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Yu L, Ma X. Trans‐external ear canal blow oxygen method. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Zsa Zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology] 2003;17(1):35‐6. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Niebuhr‐Jorgensen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Niebuhr‐Jorgensen M. Autoinflation as a treatment of otitis media in children younger than three years. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium: Recent Advances in Otitis Media with Effusion. 1996:212‐3.
Scadding 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Scadding G, Rajput K, Parikh A, Hilss S, Jansz JA, Darby YC, et al. Double blind, placebo‐controlled study of Flixonase with and without Otovent in the treatment of otitis media with effusion. 8th International Congress of Paediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 2002.
References to ongoing studies
Tel‐Aviv Med Center 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Tel‐Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. The influence of the Ear Popper on serous otitis media and the accompanying conductive hearing loss in children. Available from http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00393159. [NCT00393159]
Williamson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Williamson I, Benge S, Perera R, Turner D, Harnden H, Raftery J, et al. Study of autoinflation in 4‐11 year old school children with glue ear. Available from: http://www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN55208702 2011. [ISRCTN55208702]
Additional references
Bluestone 1988
-
- Bluestone CD, Klein JO. Otitis Media in Infants and Children. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company, 1988.
Browning 2010
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins, JPT, Altman DG. Section 8.11.2.2 Approximate analyses of cluster‐randomized trials for a meta‐analysis: effective sample sizes. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2005.
Fiellau 1977
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M, Lous J, Pedersen SV, Schousboe HH. Tympanometry in three‐year‐old children. I. A regional prevalence study on the distribution of tympanometric results in a non‐selected population of three‐year‐old children. Scandinavian Audiology 1977;6(4):199‐204. - PubMed
Fiellau 1979
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M, Lous J. Prospective tympanometry in three‐year‐old children: a study of the spontaneous course of tympanometry types in a non‐selected population. Archives of Otolaryngology 1979;105(8):461‐6. - PubMed
Fiellau 1983
-
- Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M. Tympanometry and secretory otitis media. Observations on diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment, and prevention in prospective cohort studies of three‐year‐old children [thesis]. Acta Oto‐Laryngologica. Supplement 1983;394:1‐73. - PubMed
Golz 1998
-
- Golz A, Netzer A, Angel‐Yeger B, Westerman ST, Gilbert LM, Joachims HZ. Effects of middle ear effusions on the vestibular system in children. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1998;119(6):695‐9. - PubMed
Grace 1990
-
- Grace AR, Pfleiderer AG. Dysequilibrium and otitis media with effusion: what is the association?. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1990;104(9):682‐4. - PubMed
Griffin 2011
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hunt‐Williams 1968
-
- Hunt‐Williams R. A method of maintaining middle ear ventilation in children. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1968;82:921. - PubMed
Jerger 1970
-
- Jerger J. Clinical experience with impedance audiometry. Archives of Otolaryngology 1970;92(4):311‐24. - PubMed
Lous 1981
-
- Lous J, Fiellau‐Nikolajsen M. Epidemiology of middle ear effusion and tubal dysfunction: a one‐year prospective study comprising monthly tympanometry in 387 non‐selected 7‐year‐old children. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 1981;3(4):303‐17. - PubMed
Lous 1995
-
- Lous J. Secretory otitis media in schoolchildren. Is screening for secretory otitis media advisable?. Danish Medical Bulletin 1995;42(1):71‐99. - PubMed
Reidpath 1999
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Rovers 1999
-
- Rovers MM, Zielhuis GA, Straatman H, Ingels K, Wilt GJ, Kauffman‐de Boer M. Comparison of the CAPAS and Ewing tests for screening of hearing in infants. Journal of Medical Screening 1999;6(4):188‐92. - PubMed
Simpson 2011
Teele 1989
-
- Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B. Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1989;160(1):83‐94. - PubMed
Umansky 2011
van den Aardweg 2010
van Zon 2012
Zielhuis 1989
-
- Zielhuis GA, Rach GH, Broek P. Screening for otitis media with effusion in preschool children. Lancet 1989;1(8633):311‐4. - PubMed
Zielhuis 1990
-
- Zielhuis GA, Rach GH, van‐den‐Broek P. The occurrence of otitis media with effusion in Dutch pre‐school children. Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 1990;15(2):147‐53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

