Role of T cells in the modulation of PTH action: physiological and clinical significance
- PMID: 23729167
- PMCID: PMC3815684
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-013-9960-8
Role of T cells in the modulation of PTH action: physiological and clinical significance
Abstract
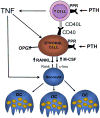
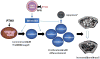
Osteoimmunology is new field of research dedicated to the study of the interactions between the immune system and bone. Among the cells of the immune system that regulate bone and hemopoietic cells are T lymphocytes. These cells secrete osteoclastogenic cytokines such as RANKL and TNF, as well as factors that stimulate bone formation and hemopoietic cells, one of which is Wnt10b. This article will review the evidence that T cells are implicated in the mechanism of action of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in bone and on the hemopoietic system.
Figures

References
-
- Riggs BL, Melton LJ. Medical progress: involutional osteoporosis. N Eng J Med. 1986;314:1676–1684. - PubMed
-
- Potts J. Primary hyperparathyroidism. In: Avioli LV, Krane S, editors. Metabolic Bone Diseases. Vol. 1. Academic Press; San Diego: 1998. pp. 411–442. #rd ed.
-
- Mazziotti G, Bilezikian J, Canalis E, Cocchi D, Giustina A. New understanding and treatments for osteoporosis. Endocrine. 2012;41(1):58–69. - PubMed
-
- Canalis E, Giustina A, Bilezikian JP. Mechanisms of anabolic therapies for osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):905–16. - PubMed
-
- Qin L, Raggatt LJ, Partridge NC. Parathyroid hormone: a double-edged sword for bone metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004;15(2):60–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

