Implication of the VirD4 coupling protein of the Lvh type 4 secretion system in virulence phenotypes of Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 23729650
- PMCID: PMC3719543
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00430-13
Implication of the VirD4 coupling protein of the Lvh type 4 secretion system in virulence phenotypes of Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
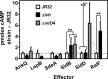
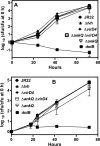
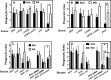
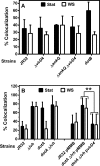
The genome of the Philadelphia-1 strain of Legionella pneumophila, the causative organism of Legionnaires' disease, encodes two virulence-associated type 4 secretion systems (T4SSs), the Dot/Icm type 4B (T4BSS) and the Lvh type 4A (T4ASS). Broth stationary-phase cultures of most dot/icm mutants are defective in entry and evasion of phagosome acidification. However, those virulence defects can be reversed by incubating broth cultures of dot/icm mutants in water, termed water stress (WS). WS reversal requires the lvh T4ASS locus, suggesting an interaction between the two T4SSs in producing Legionella virulence phenotypes. In the current work, the loss of WS reversal in a dotA Δlvh mutant of strain JR32 was shown to be attributable to loss of the lvh virD4 gene, encoding the putative coupling protein of the T4ASS. Transformation of a dotA Δlvh mutant with virD4 also reversed entry and phagosome acidification defects in broth cultures. In addition, broth cultures of Δlvh and ΔvirD4 mutants, which were dot/icm(+), showed 5-fold and >6-fold increases in translocation of the Dot/Icm translocation substrates, proteins RalF and SidD, respectively. These data demonstrate that the Lvh T4ASS functions in both broth stationary-phase cultures conventionally used for infection and cultures exposed to WS treatment. Our studies in a dotA Δlvh mutant and in a dot/icm(+) background establish that VirD4 and the Lvh T4ASS contribute to virulence phenotypes and are consistent with independent functioning of Dot/Icm and Lvh T4SSs or functional substitution of the Lvh VirD4 protein for a component(s) of the Dot/Icm T4BSS.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2011. Legionellosis—United States, 2000-2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 60:1083–1086 - PubMed
-
- Steinert M, Hentschel U, Hacker J. 2002. Legionella pneumophila: an aquatic microbe goes astray. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 26:149–162 - PubMed
-
- Ge J, Shao F. 2011. Manipulation of host vesicular trafficking and innate immune defence by Legionella Dot/Icm effectors. Cell. Microbiol. 13:1870–1880 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

