Multiple risk pathways for schizophrenia converge in serine racemase knockout mice, a mouse model of NMDA receptor hypofunction
- PMID: 23729812
- PMCID: PMC3696825
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304308110
Multiple risk pathways for schizophrenia converge in serine racemase knockout mice, a mouse model of NMDA receptor hypofunction
Abstract
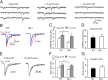
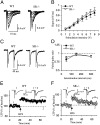
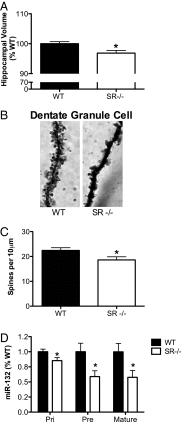
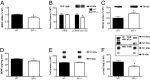
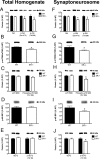
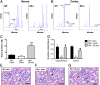
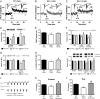
Schizophrenia is characterized by reduced hippocampal volume, decreased dendritic spine density, altered neuroplasticity signaling pathways, and cognitive deficits associated with impaired hippocampal function. We sought to determine whether this diverse pathology could be linked to NMDA receptor (NMDAR) hypofunction, and thus used the serine racemase-null mutant mouse (SR(-/-)), which has less than 10% of normal brain D-serine, an NMDAR coagonist. We found that D-serine was necessary for the maintenance of long-term potentiation in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus and for full NMDAR activity on granule cells. SR(-/-) mice had reduced dendritic spines and hippocampal volume. These morphological changes were paralleled by diminished BDNF/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and impaired performance on a trace-conditioning memory task. Chronic D-serine treatment normalized the electrophysiological, neurochemical, and cognitive deficits in SR(-/-) mice. These results demonstrate that NMDAR hypofunction can reproduce the numerous hippocampal deficits associated with schizophrenia, which can be reversed by chronic peripheral D-serine treatment.
Keywords: CREB; MeCP2; glycogen synthase 3 kinase; miR-132.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.T.C. is a consultant for Biovail, Puretech, Abbott, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and owns stock in Abbott. A patent owned by Massachusetts General Hospital for the use of
Figures
References
-
- Perälä J, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychotic and bipolar I disorders in a general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(1):19–28. - PubMed
-
- Jarskog LF, Miyamoto S, Lieberman JA. Schizophrenia: New pathological insights and therapies. Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:49–61. - PubMed
-
- Rosoklija G, et al. Structural abnormalities of subicular dendrites in subjects with schizophrenia and mood disorders: Preliminary findings. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(4):349–356. - PubMed
-
- Adriano F, Caltagirone C, Spalletta G. Hippocampal volume reduction in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia: A review and meta-analysis. Neuroscientist. 2011;18(2):180–200. - PubMed
-
- Heckers S, et al. Impaired recruitment of the hippocampus during conscious recollection in schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1(4):318–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

