Selective Kv1.3 channel blocker as therapeutic for obesity and insulin resistance
- PMID: 23729813
- PMCID: PMC3683782
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1221206110
Selective Kv1.3 channel blocker as therapeutic for obesity and insulin resistance
Abstract
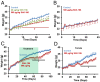
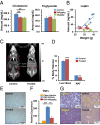
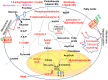
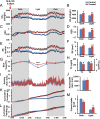
Obesity is an epidemic, calling for innovative and reliable pharmacological strategies. Here, we show that ShK-186, a selective and potent blocker of the voltage-gated Kv1.3 channel, counteracts the negative effects of increased caloric intake in mice fed a diet rich in fat and fructose. ShK-186 reduced weight gain, adiposity, and fatty liver; decreased blood levels of cholesterol, sugar, HbA1c, insulin, and leptin; and enhanced peripheral insulin sensitivity. These changes mimic the effects of Kv1.3 gene deletion. ShK-186 did not alter weight gain in mice on a chow diet, suggesting that the obesity-inducing diet enhances sensitivity to Kv1.3 blockade. Several mechanisms may contribute to the therapeutic benefits of ShK-186. ShK-186 therapy activated brown adipose tissue as evidenced by a doubling of glucose uptake, and increased β-oxidation of fatty acids, glycolysis, fatty acid synthesis, and uncoupling protein 1 expression. Activation of brown adipose tissue manifested as augmented oxygen consumption and energy expenditure, with no change in caloric intake, locomotor activity, or thyroid hormone levels. The obesity diet induced Kv1.3 expression in the liver, and ShK-186 caused profound alterations in energy and lipid metabolism in the liver. This action on the liver may underlie the differential effectiveness of ShK-186 in mice fed a chow vs. an obesity diet. Our results highlight the potential use of Kv1.3 blockers for the treatment of obesity and insulin resistance.
Keywords: brown fat; diabetes mellitus; inflammation; metabolic syndrome; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: S.K.U., K.L.E.-M., M.R.M., S.I., P.H.W., P.S.-C., J.M., and K.G.C. are coinventors of a patent on ShK-186 and obesity filed by the University of California and licensed to Kineta, Inc. S.I. is the Chief Scientific Officer of Kineta, Inc. K.G.C. owns stock options (<5%) in Kineta, Inc.
Figures






Comment in
-
Metabolic disease: potassium channel blocker prevents obesity.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Aug;12(8):577. doi: 10.1038/nrd4081. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23868114 No abstract available.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA. 2010;303(3):235–241. - PubMed
-
- Dudina A, et al. SCORE investigators Relationships between body mass index, cardiovascular mortality, and risk factors: A report from the SCORE investigators. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2011;18(5):731–742. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, et al. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 regulates energy homeostasis and body weight. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12(5):551–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

