Computational Modeling Deduced Three Dimensional Structure of Cry1Ab16 Toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis AC11
- PMID: 23729892
- PMCID: PMC3386433
- DOI: 10.1007/s12088-011-0191-5
Computational Modeling Deduced Three Dimensional Structure of Cry1Ab16 Toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis AC11
Abstract
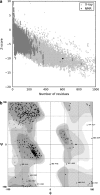
The first theoretical structural model of newly reported Cry1Ab16 δ-endotoxin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis AC11 was predicted using homology modeling technique. Cry1Ab16 resembles the Cry1Aa protein structure by sharing a common three domains structure responsible in pore forming and specificity determination along with few structural deviations. The main differences between the two is in the length of loops, absence of α7b, α9a, α10b, α11a and presence of additional β12b, α13 components while α10a is spatially located at downstream position in Cry1Ab16. A better understanding of the 3D structure shall be helpful in the design of domain swapping and mutagenesis experiments aimed at improving toxicity.
Keywords: Cry toxins; Insecticidal crystal protein; Receptor insertion; Third-party annotation; α-Helical bundle.
Figures


References
-
- Hofmann C, Vanderbruggen H, Hofte H, Rie J, Jansens S, Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins is correlated with the presence of high-affinity binding sites in the brush border membrane of target insect midgets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7844. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knowles BH, Ellar DJ. Colloid osmotic lysis is a general feature of the mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins with different insect specificities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;924:509–518. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90167-X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
