Telmisartan/Hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy for the treatment of hypertension: a pooled analysis in older and younger patients
- PMID: 23730986
- PMCID: PMC8033787
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12089
Telmisartan/Hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy for the treatment of hypertension: a pooled analysis in older and younger patients
Abstract
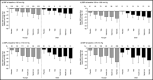
Older patients frequently receive angiotensin II receptor blocker/diuretic combinations to control blood pressure (BP), although there have been relatively few trials specifically examining this patient population. A pooled analysis was performed of data from 7 randomized trials of telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide combinations or telmisartan monotherapy in older (65 years and older) and younger (younger than 65 years) patients to better understand the response of older patients to a telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination. Telmisartan doses were 40 mg and 80 mg (T40 and T80). Hydrochlorothiazide doses were 12.5 mg and 25 mg (H12.5 and H25). A total of 3654 patients were included and the mean treatment duration was approximately 8 weeks. BP reductions with telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide combinations were broadly similar in older and younger patients. In older patients, mean BP reductions from baseline were -30.1/-19.0 mm Hg with the T80/H25 combination and -21.7/-13.0 mm Hg with T80 monotherapy. Tolerability was similar regardless of age, and the incidence of adverse events in both older and younger patients was similar to placebo. The telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination, particularly high-dose T80/H25, is effective and well tolerated in patients 65 years and older as well as in younger patients.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Lim MA, Townsend RR. Arterial compliance in the elderly: its effect on blood pressure measurement and cardiovascular outcomes. Clin Geriatr Med. 2009;25:191–205. - PubMed
-
- Aronow WS, Fleg JL, Pepine CJ, et al. ACCF/AHA 2011 expert consensus document on hypertension in the elderly: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus documents developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Neurology, American Geriatrics Society, American Society for Preventive Cardiology, American Society of Hypertension, American Society of Nephrology, Association of Black Cardiologists, and European Society of Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:2037–2114. - PubMed
-
- Pimenta E, Oparil S. Management of hypertension in the elderly. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012;9:286–296. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

