Lineages of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi in the Irish equine industry
- PMID: 23731628
- PMCID: PMC3679875
- DOI: 10.1186/2046-0481-66-10
Lineages of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi in the Irish equine industry
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus equi ssp. equi is the causative agent of 'Strangles' in horses. This is a debilitating condition leading to economic loss, yard closures and cancellation of equestrian events. There are multiple genotypes of S. equi ssp. equi which can cause disease, but to date there has been no systematic study of strains which are prevalent in Ireland. This study identified and classified Streptococcus equi ssp. equi strains isolated from within the Irish equine industry.
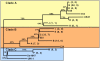
Results: Two hundred veterinary isolates were subjected to SLST (single locus sequence typing) based on an internal sequence from the seM gene of Streptococcus equi ssp equi. Of the 171 samples which successfully gave an amplicon, 162 samples (137 Irish and 24 UK strains) gave robust DNA sequence information. Analysis of the sequences allowed division of the isolates into 19 groups, 13 of which contain at least 2 isolates and 6 groups containing single isolates. There were 19 positions where a DNA SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) occurs, and one 3 bp insertion. All groups had multiple (2-8) SNPs. Of the SNPs 17 would result in an amino acid change in the encoded protein. Interestingly, the single isolate EI8, which has 6 SNPs, has the three base pair insertion which is not seen in any other isolate, this would result in the insertion of an Ile residue at position 62 in that protein sequence. Comparison of the relevant region in the determined sequences with the UK Streptococcus equi seM MLST database showed that Group B (15 isolates) and Group I (2 isolates), as well as the individual isolates EI3 and EI8, are unique to Ireland, and some groups are most likely of UK origin (Groups F and M), but many more probably passed back and forth between the two countries.
Conclusions: The strains occurring in Ireland are not clonal and there is a considerable degree of sequence variation seen in the seM gene. There are two major clades causing infection in Ireland and these strains are also common in the UK.
Keywords: Strangles; Streptococcus equi ssp. equi; seM.
Figures
References
-
- Meehan M, Muldowney DA, Watkins NJ, Owen P. Localization and characterization of the ligand-binding domain of the fibrinogen-binding protein (FgBP) of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. Microbiology. 2000;146(Pt 5):1187–1194. - PubMed
-
- Kelly C, Bugg M, Robinson C, Mitchell Z, Davis-Poynter N, Newton JR, Jolley KA, Maiden MC, Waller AS. Sequence variation of the SeM gene of Streptococcus equi allows discrimination of the source of strangles outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:480–486. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.2.480-486.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

