Screening of osteoprotegerin-related feature genes in osteoporosis and functional analysis with DNA microarray
- PMID: 23731710
- PMCID: PMC3735399
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-18-15
Screening of osteoprotegerin-related feature genes in osteoporosis and functional analysis with DNA microarray
Abstract
Background: Osteoporosis affects 200 million people worldwide and places an enormous economic burden on society. We aim to identify the feature genes that are related to osteoprotegerin in osteoporosis and to perform function analysis with DNA microarray from human bone marrow.
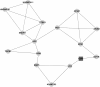
Methods: We downloaded the gene expression profile GSE35957 from Gene Expression Omnibus database including nine gene chips from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of five osteoporotic and four non-osteoporotic subjects. The differentially expressed genes between normal and disease samples were identified by LIMMA package in R language. The interactions among the osteoprotegerin gene (OPG) and differentially expressed genes were searched and visualized by Cytoscape. MCODE and Bingo were used to perform module analysis. Finally, GENECODIS was used to obtain enriched pathways of genes in an interaction network.
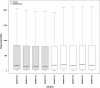
Results: A total of 656 genes were identified as differentially expressed genes between osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic samples. IL17RC, COL1A1, and ESR1 were identified to interact with OPG directly from the protein-protein interaction network. A module containing ERS1 was screened out, and this module was most significantly enriched in organ development. Pathway enrichment analysis suggested genes in the interaction network were related to focal adhesion.
Conclusions: The expression pattern of IL17RC, COL1A1, and ESR1 can be useful in osteoporosis detection, which may help in identifying those populations at high risk for osteoporosis, and in directing treatment of osteoporosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening and functional microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes related to osteoporosis.Genet Mol Res. 2014 Apr 25;13(2):3228-36. doi: 10.4238/2014.April.25.8. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 24841655
-
Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of mesenchymal stem cells in elderly patients with osteoporosis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015 Oct;27(5):595-601. doi: 10.1007/s40520-015-0346-z. Epub 2015 Mar 15. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 25771989
-
Identification of transcriptional factors and key genes in primary osteoporosis by DNA microarray.Med Sci Monit. 2015 May 9;21:1333-44. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894111. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 25957414 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interaction network and significant gene analysis of osteoporosis.Genet Mol Res. 2013 Oct 18;12(4):4751-9. doi: 10.4238/2013.October.18.12. Genet Mol Res. 2013. PMID: 24222250
-
Analysis of protein-protein interaction network and functional modules on primary osteoporosis.Eur J Med Res. 2014 Mar 21;19(1):15. doi: 10.1186/2047-783X-19-15. Eur J Med Res. 2014. Retraction in: Eur J Med Res. 2015 Mar 26;20:33. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0128-2. PMID: 24656062 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
P4 medicine and osteoporosis: a systematic review.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016 Dec;128(Suppl 7):480-491. doi: 10.1007/s00508-016-1125-3. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016. PMID: 27873024
-
Changes in Human Foetal Osteoblasts Exposed to the Random Positioning Machine and Bone Construct Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 18;20(6):1357. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061357. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30889841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura M, Udagawa N. Osteoporosis and RANKL signal. Clin Calcium. 2011;21:1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Sweet DE, Reger SI, Thompson RC. Fat-cell changes as a mechanism of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in cortisone-treated rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:729–735. - PubMed
-
- Martin R, Zissimes SL. Relationships between marrow fat and bone turnover in ovariectomized and intact rats. Bone. 1991;12:123–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

