Neutrophil roles in left ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction
- PMID: 23731794
- PMCID: PMC3681584
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-6-11
Neutrophil roles in left ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction
Abstract
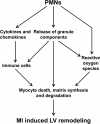
Polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMNs; neutrophils) serve as key effector cells in the innate immune system and provide the first line of defense against invading microorganisms. In addition to producing inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and undergoing a respiratory burst that stimulates the release of reactive oxygen species, PMNs also degranulate to release components that kill pathogens. Recently, neutrophil extracellular traps have been shown to be an alternative way to trap microorganisms and contain infection. PMN-derived granule components are also involved in multiple non-infectious inflammatory processes, including the response to myocardial infarction (MI). In this review, we will discuss the biological characteristics, recruitment, activation, and removal of PMNs, as well as the roles of PMN-derived granule proteins in inflammation and innate immunity, focusing on the MI setting when applicable. We also discuss future perspectives that will direct research in PMN biology.
Figures


References
-
- Akpek M, Kaya MG, Lam YY, Sahin O, Elcik D, Celik T, Ergin A, Gibson CM. Relation of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio to coronary flow to in-hospital major adverse cardiac events in patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction undergoing primary coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:621–627. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.04.041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chia S, Nagurney JT, Brown DF, Raffel OC, Bamberg F, Senatore F, Wackers FJ, Jang IK. Association of leukocyte and neutrophil counts with infarct size, left ventricular function and outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:333–337. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.09.085. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

