HIF-1α knockdown by miRNA decreases survivin expression and inhibits A549 cell growth in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23732337
- PMCID: PMC3776716
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1405
HIF-1α knockdown by miRNA decreases survivin expression and inhibits A549 cell growth in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
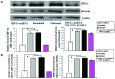
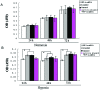
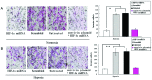
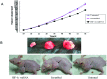
The present study examined the downregulation of survivin expression by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) miRNA and its effect in the inhibition of A549 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Survivin expression, apoptosis, proliferation and migration under normoxic and hypoxic conditions were assessed by standard methods. Cotransfection and chromatin immunoprecipitation were used to observe the effects of HIF-1α on survivin transcription. HIF-1α knockdown in A549 cells were injected into nude mice to examine survivin expression and suppression of tumorigenicity. Transfection of A549 cells with HIF-1α miRNA led to decreased expression of HIF-1α and survivin mRNA and protein. Survivin overexpression is mediated by HIF-1α by direct binding to a putative binding site in the survivin core promoter. HIF-1α-miRNA induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation of A549 cells under hypoxic, but not normoxic, conditions, whereas transfection by survivin expression vectors partly rescued the apoptotic phenotype and revived cell proliferation under hypoxic conditions. However, cell migration was substantially suppressed by HIF-1α silencing under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. After A549 cells were xenografted in nude mice, survivin expression in mice treated with HIF-1α miRNA was downregulated, and tumor growth was significantly inhibited. Silenced HIF-1α gene expression induced apoptosis and suppressed growth of A549 cells by downregulating survivin expression in vitro and in vivo. Our results also provide a basis to target the HIF-1α pathway in lung cancer therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN. Apoptosis: mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Ann Hematol. 2005;84:627–639. - PubMed
-
- Altieri DC. The molecular basis and potential role of survivin in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:542–547. - PubMed
-
- Rodel F, Hoffmann J, Distel L, et al. Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4881–4887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

