Receptor tyrosine kinases in Drosophila development
- PMID: 23732470
- PMCID: PMC3660834
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009050
Receptor tyrosine kinases in Drosophila development
Abstract
Tyrosine phosphorylation plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. The Drosophila genome encodes more than 20 receptor tyrosine kinases and extensive studies in the past 20 years have illustrated their diverse roles and complex signaling mechanisms. Although some receptor tyrosine kinases have highly specific functions, others strikingly are used in rather ubiquitous manners. Receptor tyrosine kinases regulate a broad expanse of processes, ranging from cell survival and proliferation to differentiation and patterning. Remarkably, different receptor tyrosine kinases share many of the same effectors and their hierarchical organization is retained in disparate biological contexts. In this comprehensive review, we summarize what is known regarding each receptor tyrosine kinase during Drosophila development. Astonishingly, very little is known for approximately half of all Drosophila receptor tyrosine kinases.
Figures
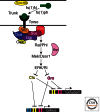
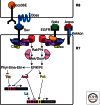
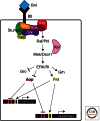
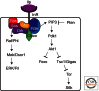
References
-
- Abrescia C, Sjostrand D, Kjaer S, Ibanez CF 2005. Drosophila RET contains an active tyrosine kinase and elicits neurotrophic activities in mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 579: 3789–3796 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad SM, Baker BS 2002. Sex-specific deployment of FGF signaling in Drosophila recruits mesodermal cells into the male genital imaginal disc. Cell 109: 651–661 - PubMed
-
- Almudi I, Stocker H, Hafen E, Corominas M, Serras F 2009. SOCS36E specifically interferes with sevenless signaling during Drosophila eye development. Dev Biol 326: 212–223 - PubMed
-
- Almudi I, Corominas M, Serras F 2010. Competition between SOCS36E and Drk modulates sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase activity. J Cell Sci 123: 3857–3862 - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio L, Mahowald AP, Perrimon N 1989a. l(1)pole hole is required maternally for pattern formation in the terminal regions of the embryo. Development 106: 145–158 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
