Spirometry in children
- PMID: 23732636
- PMCID: PMC6442789
- DOI: 10.4104/pcrj.2013.00042
Spirometry in children
Abstract
Respiratory disorders are responsible for considerable morbidity and mortality in children. Spirometry is a useful investigation for diagnosing and monitoring a variety of paediatric respiratory diseases, but it is underused by primary care physicians and paediatricians treating children with respiratory disease. We now have a better understanding of respiratory physiology in children, and newer computerised spirometry equipment is available with updated regional reference values for the paediatric age group. This review evaluates the current literature for indications, test procedures, quality assessment, and interpretation of spirometry results in children. Spirometry may be useful for asthma, cystic fibrosis, congenital or acquired airway malformations and many other respiratory diseases in children. The technique for performing spirometry in children is crucial and is discussed in detail. Most children, including preschool children, can perform acceptable spirometry. Steps for interpreting spirometry results include identification of common errors during the test by applying acceptability and repeatability criteria and then comparing test parameters with reference standards. Spirometry results depict only the pattern of ventilation, which may be normal, obstructive, restrictive, or mixed. The diagnosis should be based on both clinical features and spirometry results. There is a need to encourage primary care physicians and paediatricians treating respiratory diseases in children to use spirometry after adequate training.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Figures
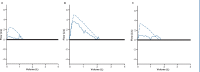
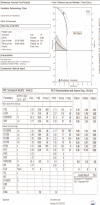
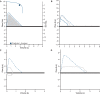
References
-
- Kotecha SJ, Watkins WJ, Paranjothy S, Dunstan FD, Henderson AJ, Kotecha S. Effect of late preterm birth on longitudinal lung spirometry in school age children and adolescents. Thorax 2012;67(1):54–61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200329 - PubMed
-
- Chhabra SK, Vijayan VK, Rahman M, Mittal V, Singh PD. Regression equations for spirometry in children aged 6 to 17 years in Delhi region. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2012;54(1):59–63. - PubMed
-
- Kirkby J, Welsh L, Lum S, et al. The EPICure study: comparison of pediatric spirometry in community and laboratory settings. Pediatr Pulmonol 2008;43(12):1233–41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ppul.20950 - PubMed
-
- Zanconato S, Meneghelli G, Braga R, Zacchello F, Baraldi E. Office spirometry in primary care pediatrics: a pilot study. Pediatrics 2005;116(6):e792–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2005-0487 - PubMed
-
- Dombkowski KJ, Hassan F, Wasilevich EA, Clark SJ. Spirometry use among pediatric primary care physicians. Pediatrics 2010;126(4):682–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-0362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
