Antidepressant effects of AMPA and ketamine combination: role of hippocampal BDNF, synapsin, and mTOR
- PMID: 23732839
- PMCID: PMC3805670
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-013-3153-2
Antidepressant effects of AMPA and ketamine combination: role of hippocampal BDNF, synapsin, and mTOR
Abstract
Rationale: A number of preclinical and clinical studies suggest that ketamine, a glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, has a rapid and lasting antidepressant effect when administered either acutely or chronically. It has been postulated that this effect is due to stimulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors.
Objective: In this study, we tested whether AMPA alone has an antidepressant effect and if the combination of AMPA and ketamine provides added benefit in Wistar-Kyoto rats, a putative animal model of depression.
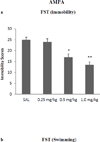
Results: Chronic AMPA treatment resulted in a dose-dependent antidepressant effect in both the forced swim test and sucrose preference test. Moreover, chronic administration (10-11 days) of combinations of AMPA and ketamine, at doses that were ineffective on their own, resulted in a significant antidepressant effect. The behavioral effects were associated with increases in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor, synapsin, and mammalian target of rapamycin.
Conclusion: These findings are the first to provide evidence for an antidepressant effect of AMPA and suggest the usefulness of AMPA-ketamine combination in treatment of depression. Furthermore, these effects appear to be associated with increases in markers of hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, suggesting a mechanism of their action.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures











References
-
- aan het Rot M, Collins KA, Murrough JW, Perez AM, Reich DL, Charney DS, Mathew SJ. Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Alt A, Nisenbaum ES, Bleakman D, Witkin JM. A role for AMPA receptors in mood disorders. Biochem. Pharmacology. 2006;71:1273–1288. - PubMed
-
- Banasr M, Soumier A, Hery M, Mocaër E, Daszuta A. Agomelatine, a New Antidepressant, Induces Regional Changes in Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:1087–1096. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47:351–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

