Why is organ transplantation clinically important?
- PMID: 23732857
- PMCID: PMC3662355
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a014985
Why is organ transplantation clinically important?
Abstract
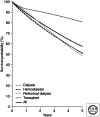
Solid organ transplantations save lives in patients affected by terminal organ failures and improve quality of life. Organ transplantations have gradually ameliorated in the last two decades and usually provide excellent results in children and young adults, and are increasingly challenged by the growing proportion of elderly transplant patients with comorbidities. Renal transplantation increases patient survival over dialysis, and lifesaving transplants are indispensible to treat patients with liver, heart, or lung irreversible diseases. Solid organ transplant programs activity has been steadily growing but is still far from global needs, with great differences among countries. Solid organ transplantations are essential for developed and mature health care systems.
Figures
References
-
- Allen RD, Al-Harbi IS, Morris JG 1997. Diabetic neuropathy after pancreas transplantation: Determinants of recovery. Transplantation 63: 830–838 - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Benden C, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Stehlik J, Hertz MI, International Society of Heart, et al. 2012. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart–lung transplant report—2012. J Heart Lung Transplant 31: 1073–1086 - PubMed
-
- Davis CL 2010. Preemptive transplantation and the transplant first initiative. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19: 592–597 - PubMed
-
- Dehennault M 2011. Paediatric features in childhood renal transplantation: Quality of life, school, adherence, transfer to adult nephrologists. Nephrol Ther 7: 599–603 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical