708 Common and 2010 rare DISC1 locus variants identified in 1542 subjects: analysis for association with psychiatric disorder and cognitive traits
- PMID: 23732877
- PMCID: PMC4031635
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.68
708 Common and 2010 rare DISC1 locus variants identified in 1542 subjects: analysis for association with psychiatric disorder and cognitive traits
Abstract
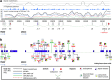
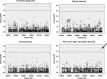
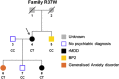
A balanced t(1;11) translocation that transects the Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) gene shows genome-wide significant linkage for schizophrenia and recurrent major depressive disorder (rMDD) in a single large Scottish family, but genome-wide and exome sequencing-based association studies have not supported a role for DISC1 in psychiatric illness. To explore DISC1 in more detail, we sequenced 528 kb of the DISC1 locus in 653 cases and 889 controls. We report 2718 validated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of which 2010 have a minor allele frequency of <1%. Only 38% of these variants are reported in the 1000 Genomes Project European subset. This suggests that many DISC1 SNPs remain undiscovered and are essentially private. Rare coding variants identified exclusively in patients were found in likely functional protein domains. Significant region-wide association was observed between rs16856199 and rMDD (P=0.026, unadjusted P=6.3 × 10(-5), OR=3.48). This was not replicated in additional recurrent major depression samples (replication P=0.11). Combined analysis of both the original and replication set supported the original association (P=0.0058, OR=1.46). Evidence for segregation of this variant with disease in families was limited to those of rMDD individuals referred from primary care. Burden analysis for coding and non-coding variants gave nominal associations with diagnosis and measures of mood and cognition. Together, these observations are likely to generalise to other candidate genes for major mental illness and may thus provide guidelines for the design of future studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rare disruptive variants in the DISC1 Interactome and Regulome: association with cognitive ability and schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 May;23(5):1270-1277. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.115. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28630456 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the TRAX/DISC locus and both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia in the Scottish population.Mol Psychiatry. 2005 Jul;10(7):657-68, 616. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001669. Mol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15838535
-
The DISC locus in psychiatric illness.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Jan;13(1):36-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002106. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17912248 Review.
-
Association between a disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) single nucleotide polymorphism and schizophrenia in a combined Scandinavian case-control sample.Schizophr Res. 2008 Dec;106(2-3):237-41. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2008.08.024. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Schizophr Res. 2008. PMID: 18818052
-
Identification of high risk DISC1 protein structural variants in patients with bipolar spectrum disorder.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Dec 17;486(3):136-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.027. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20850505 Review.
Cited by
-
Category fluency, latent semantic analysis and schizophrenia: a candidate gene approach.Cortex. 2014 Jun;55:182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Cortex. 2014. PMID: 24447899 Free PMC article.
-
Upstream Pathways Controlling Mitochondrial Function in Major Psychosis: A Focus on Bipolar Disorder.Can J Psychiatry. 2016 Aug;61(8):446-56. doi: 10.1177/0706743716648297. Epub 2016 May 9. Can J Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27310240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Miro GTPases coordinate mitochondrial and peroxisomal dynamics.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):372-398. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1843957. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33183150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of schizophrenia.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014 Nov;16(11):502. doi: 10.1007/s11920-014-0502-8. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014. PMID: 25200985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FASTKD2 is associated with memory and hippocampal structure in older adults.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Oct;20(10):1197-204. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.142. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25385369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottesman II, Laursen TM, Bertelsen A, Mortensen PB. Severe mental disorders in offspring with 2 psychiatrically ill parents. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:252–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

