The function of importin β1 is conserved in eukaryotes but the substrates may vary in organisms
- PMID: 23733071
- PMCID: PMC3999071
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.25106
The function of importin β1 is conserved in eukaryotes but the substrates may vary in organisms
Abstract
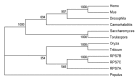
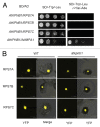
Importin β1 is the nuclear-cytoplasmic transport receptor in eukaryotic cells. Its main function is to transport NLS (nuclear localization signal)-containing proteins from cytoplasm to nucleus. Our recent study found that AtKPNB1, a homolog of the human KPNB1, is an essential component of the classical nuclear import of the NLS-containing proteins in Arabidopsis and modulates plant development and ABA-mediated stress response. Human KPNB1 can also directly transport the nuclear proteins, such as ribosomal protein RPS7e, without the intervention of importin α proteins. However, we found that AtKPNB1 does not directly recognize and import the human RPS7e homologous proteins AtRPS7A, AtRPS7B and AtRPS7C into the nucleus like human KPNB1. These findings suggest that the importin β1 protein has the conserved function in translocating nuclear proteins to the nucleus, but their specific cargos may vary in different organisms.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; NLS-containing protein; importin α; importin β1; nuclear-cytoplasmic transport.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
