Hydrogels that mimic developmentally relevant matrix and N-cadherin interactions enhance MSC chondrogenesis
- PMID: 23733927
- PMCID: PMC3690835
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214100110
Hydrogels that mimic developmentally relevant matrix and N-cadherin interactions enhance MSC chondrogenesis
Abstract
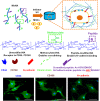
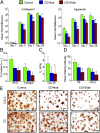
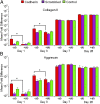
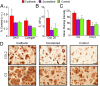
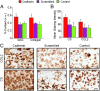
Methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels provide a backbone polymer with which mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can interact through several cell surface receptors that are expressed by MSCs, including CD44 and CD168. Previous studies showed that this 3D hydrogel environment supports the chondrogenesis of MSCs, and here we demonstrate through functional blockade that these specific cell-material interactions play a role in this process. Beyond matrix interactions, cadherin molecules, a family of transmembrane glycoproteins, play a critical role in tissue development during embryogenesis, and N-cadherin is a key factor in mediating cell-cell interactions during mesenchymal condensation and chondrogenesis. In this study, we functionalized HA hydrogels with N-cadherin mimetic peptides and evaluated their role in regulating chondrogenesis and cartilage matrix deposition by encapsulated MSCs. Our results show that conjugation of cadherin peptides onto HA hydrogels promotes both early chondrogenesis of MSCs and cartilage-specific matrix production with culture, compared with unmodified controls or those with inclusion of a scrambled peptide domain. This enhanced chondrogenesis was abolished via treatment with N-cadherin-specific antibodies, confirming the contribution of these N-cadherin peptides to chondrogenesis. Subcutaneous implantation of MSC-seeded constructs also showed superior neocartilage formation in implants functionalized with N-cadherin mimetic peptides compared with controls. This study demonstrates the inherent biologic activity of HA-based hydrogels, as well as the promise of biofunctionalizing HA hydrogels to emulate the complexity of the natural cell microenvironment during embryogenesis, particularly in stem cell-based cartilage regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641–650. - PubMed
-
- Rogers JJ, Young HE, Adkison LR, Lucas PA, Black AC., Jr Differentiation factors induce expression of muscle, fat, cartilage, and bone in a clone of mouse pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells. Am Surg. 1995;61(3):231–236. - PubMed
-
- Connelly JT, García AJ, Levenston ME. Inhibition of in vitro chondrogenesis in RGD-modified three-dimensional alginate gels. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):1071–1083. - PubMed
-
- Lee HJ, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells in collagen mimetic peptide-mediated microenvironment. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(11):1843–1851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

