RNA-binding proteins and translational regulation in axons and growth cones
- PMID: 23734093
- PMCID: PMC3661996
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00081
RNA-binding proteins and translational regulation in axons and growth cones
Abstract
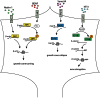
RNA localization and regulation play an important role in the developing and adult nervous system. In navigating axons, extrinsic cues can elicit rapid local protein synthesis that mediates directional or morphological responses. The mRNA repertoire in axons is large and dynamically changing, yet studies suggest that only a subset of these mRNAs are translated after cue stimulation, suggesting the need for a high level of translational regulation. Here, we review the role of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) as local regulators of translation in developing axons. We focus on their role in growth, guidance, and synapse formation, and discuss the mechanisms by which they regulate translation in axons.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; axon guidance; axon outgrowth; local translation; synapse formation.
Figures
References
-
- Akker S. A., Misra S., Aslam S., Morgan E. L., Smith P. J., Khoo B., et al. (2007). Pre-spliceosomal binding of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and heterogenous nuclear RNP E1 is associated with suppression of a growth hormone receptor pseudoexon. Mol. Endocrinol. 21, 2529–2540 10.1210/me.2007-0038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albers C. A., Paul D. S., Schulze H., Freson K., Stephens J. C., Smethurst P. A., et al. (2012). Compound inheritance of a low-frequency regulatory SNP and a rare null mutation in exon-junction complex subunit RBM8A causes TAR syndrome. Nat. Genet. 44, 435–439, S1–S2. 10.1038/ng.1083 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

