Evasion of adaptive and innate immune response mechanisms by γ-herpesviruses
- PMID: 23735334
- PMCID: PMC4397892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.05.011
Evasion of adaptive and innate immune response mechanisms by γ-herpesviruses
Abstract
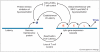
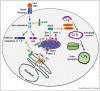
γ-Herpesviral immune evasion mechanisms are optimized to support the acute, lytic and the longterm, latent phase of infection. During acute infection, specific immune modulatory proteins limit, but also exploit, the antiviral activities of cell intrinsic innate immune responses as well as those of innate and adaptive immune cells. During latent infection, a restricted gene expression program limits immune targeting and cis-acting mechanisms to reduce the antigen presentation as well as antigenicity of latency-associated proteins. Here, we will review recent progress in our understanding of γ-herpesviral immune evasion strategies.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune escape of γ-herpesviruses from adaptive immunity.Rev Med Virol. 2014 Nov;24(6):365-78. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1791. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Rev Med Virol. 2014. PMID: 24733560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune evasion by gamma-herpesviruses.Curr Opin Immunol. 2004 Aug;16(4):456-62. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2004.05.002. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15245739 Review.
-
A gamma-herpesvirus deficient in replication establishes chronic infection in vivo and is impervious to restriction by adaptive immune cells.Virology. 2006 Sep 15;353(1):210-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.05.020. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16797052
-
Natural history of murine gamma-herpesvirus infection.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001 Apr 29;356(1408):569-79. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0779. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11313012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and Evasion of Innate Immunity by Gammaherpesviruses.J Mol Biol. 2022 Mar 30;434(6):167214. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167214. Epub 2021 Aug 23. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34437888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Critical Role of Genome Maintenance Proteins in Immune Evasion During Gammaherpesvirus Latency.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 9;9:3315. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03315. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30687291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of Protein Deamidation in Innate Immune Signaling.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4262-4268. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01980-15. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26889032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpesvirus microRNAs for use in gene therapy immune-evasion strategies.Gene Ther. 2017 Jul;24(7):385-391. doi: 10.1038/gt.2017.37. Epub 2017 May 9. Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28485720 Review.
-
DNAM-1 Activating Receptor and Its Ligands: How Do Viruses Affect the NK Cell-Mediated Immune Surveillance during the Various Phases of Infection?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 30;20(15):3715. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153715. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31366013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection and lytic reactivation of herpesviruses: A potential threat in the postpandemic era?J Med Virol. 2022 Nov;94(11):5103-5111. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27994. Epub 2022 Jul 22. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 35819034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freeman ML, Lanzer KG, Cookenham T, Peters B, Sidney J, et al. Two kinetic patterns of epitope-specific CD8 T-cell responses following murine gammaherpesvirus 68 infection. J Virol. 2010;84:2881–2892. The authors identified a range of novel H-2(b) restricted epitopes and showed that the T cell response to these epitopes falls into two kinetic classes based on the speed of decline. The slowly declining response corresponded to the latent phase since decline was accelerated when mice were infected with a virus unable to establish latency. This suggests that T cell responses mirror the viral life cycle. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blake N. Immune evasion by gammaherpesvirus genome maintenance proteins. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:829–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

