Survival of patients with superficial esophageal adenocarcinoma after endoscopic treatment vs surgery
- PMID: 23735443
- PMCID: PMC3889479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.05.025
Survival of patients with superficial esophageal adenocarcinoma after endoscopic treatment vs surgery
Abstract
Background & aims: Endoscopic therapy can improve long-term outcomes of patients with superficial esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), producing fewer complications than esophagectomy. However, there have been few population-based studies to compare long-term outcomes of patients who received these treatments. We used a large national cancer database to evaluate the outcomes of patients with superficial EAC who underwent endoscopic therapy or surgery.
Methods: We used the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results database to identify 1618 patients with Tis or T1 N0M0 EAC from 1998-2009. Patients were grouped on the basis of whether they received endoscopic therapy (n = 306) or surgery (n = 1312). Multivariate logistic regression was performed to identify factors associated with endoscopic therapy. We collected survival data through the end of 2009; overall survival and esophageal cancer-specific survival were compared after controlling for relevant covariates.
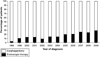
Results: The use of endoscopic therapy increased progressively from 3% in 1998 to 29% in 2009. Factors associated with use of endoscopic therapy included age older than 65 years, diagnosis in 2006-2009 vs 1998-2001, and the absence of submucosal invasion. Overall survival after 5 years was higher in the surgery group than in the endoscopic therapy group (70% vs 58%, respectively). After adjusting for patient and tumor factors, patients treated by endoscopy had similar overall survival times (hazard ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.92-1.58) and esophageal cancer-specific survival times (hazard ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.49-1.11).
Conclusion: In a population-based analysis, the use of endoscopic therapy for superficial EAC tended to increase from 1998-2009. Long-term survival of patients with EAC did not appear to differ between those who received endoscopic therapy and those treated with surgery.
Keywords: CI; Database Analysis; EAC; ET; Endoscopic Therapy; Esophageal Cancer; HGD; HR; OR; RFA; Retrospective Study; SEER; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results; confidence interval; endoscopic therapy; esophageal adenocarcinoma; hazard ratio; high-grade dysplasia; odds ratio; radiofrequency ablation.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Thrift AP, Whiteman DC. The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma continues to rise: analysis of period and birth cohort effects on recent trends. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:3155–3162. - PubMed
-
- Eloubeidi MA, Mason AC, Desmond RA, El-Serag HB. Temporal trends (1973–1997) in survival of patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma in the United States: a glimmer of hope? Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1627–1633. - PubMed
-
- Chang AC, Ji H, Birkmeyer NJ, Orringer MB, Birkmeyer JD. Outcomes after transhiatal and transthoracic esophagectomy for cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P, Doddoli C, Neville P, et al. Esophageal cancer resection in the elderly. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1996;10:941–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical