Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 23735727
- PMCID: PMC3781504
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0387
Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
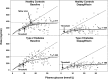
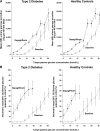
Objective: To examine the effect of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, on the major components of renal glucose reabsorption (decreased maximum renal glucose reabsorptive capacity [TmG], increased splay, and reduced threshold), using the pancreatic/stepped hyperglycemic clamp (SHC) technique.
Research design and methods: Subjects with type 2 diabetes (n=12) and matched healthy subjects (n=12) underwent pancreatic/SHC (plasma glucose range 5.5-30.5 mmol/L) at baseline and after 7 days of dapagliflozin treatment. A pharmacodynamic model was developed to describe the major components of renal glucose reabsorption for both groups and then used to estimate these parameters from individual glucose titration curves.
Results: At baseline, type 2 diabetic subjects had elevated TmG, splay, and threshold compared with controls. Dapagliflozin treatment reduced the TmG and splay in both groups. However, the most significant effect of dapagliflozin was a reduction of the renal threshold for glucose excretion in type 2 diabetic and control subjects.
Conclusions: The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin improves glycemic control in diabetic patients by reducing the TmG and threshold at which glucose is excreted in the urine.
Figures

References
-
- Valtin H. Renal Function: Mechanism Preserving Fluid and Solute Balance in Health Boston, Little, Brown and Company, 1983
-
- Wright EM, Loo DD, Hirayama BA. Biology of human sodium glucose transporters. Physiol Rev 2011;91:733–794 - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2011;32:515–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

