miRNA-548c: a specific signature in circulating PBMCs from dilated cardiomyopathy patients
- PMID: 23735785
- PMCID: PMC3735826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.05.011
miRNA-548c: a specific signature in circulating PBMCs from dilated cardiomyopathy patients
Abstract
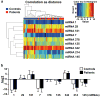
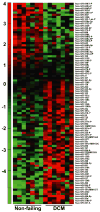
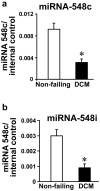
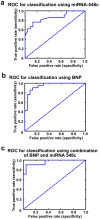
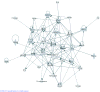
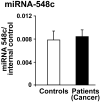
High fidelity genome-wide expression analysis has strengthened the idea that microRNA (miRNA) signatures in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) can be potentially used to predict the pathology when anatomical samples are inaccessible like the heart. PBMCs from 48 non-failing controls and 44 patients with relatively stable chronic heart failure (ejection fraction of ≤ 40%) associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) were used for miRNA analysis. Genome-wide miRNA-microarray on PBMCs from chronic heart failure patients identified miRNA signature uniquely characterized by the downregulation of miRNA-548 family members. We have also independently validated downregulation of miRNA-548 family members (miRNA-548c & 548i) using real time-PCR in a large cohort of independent patient samples. Independent in silico Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of miRNA-548 targets shows unique enrichment of signaling molecules and pathways associated with cardiovascular disease and hypertrophy. Consistent with specificity of miRNA changes with pathology, PBMCs from breast cancer patients showed no alterations in miRNA-548c expression compared to healthy controls. These studies suggest that miRNA-548 family signature in PBMCs can therefore be used to detect early heart failure. Our studies show that cognate networking of predicted miRNA-548 targets in heart failure can be used as a powerful ancillary tool to predict the ongoing pathology.
Keywords: Biomarker; Canonical signaling networks; Dilated cardiomyopathy; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC); microRNA-548.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA signatures in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronic heart failure patients.Physiol Genomics. 2010 Aug;42(3):420-6. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00211.2009. Epub 2010 May 18. Physiol Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20484156
-
Unique microRNA profile in end-stage heart failure indicates alterations in specific cardiovascular signaling networks.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27487-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.036541. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 15;291(29):14914. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A109.036541. PMID: 19641226 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Identification of micro-RNA networks in end-stage heart failure because of dilated cardiomyopathy.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Sep;17(9):1173-87. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12096. Epub 2013 Sep 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23998897 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs--regulators of signaling networks in dilated cardiomyopathy.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Jun;3(3):225-34. doi: 10.1007/s12265-010-9177-7. Epub 2010 May 1. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20560044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of microRNAs in dilated cardiomyopathy: evidence regarding etiology.Transl Res. 2020 Jan;215:86-101. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 31505160 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA Expression in Prospectively Collected Blood as a Potential Biomarker of Breast Cancer Risk in the BCFR.Anticancer Res. 2015 Jul;35(7):3969-77. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26124344 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-132 controls pancreatic beta cell proliferation and survival through Pten/Akt/Foxo3 signaling.Mol Metab. 2020 Jan;31:150-162. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31918917 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction.World J Cardiol. 2015 Dec 26;7(12):843-60. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.843. World J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26730290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs as biomarkers for diagnosis of heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(22):e6825. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006825. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28562533 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of microRNA expression profiling studies in heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Jul;26(4):997-1021. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10071-9. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 33443726 Review.
References
-
- van Rooij E, Liu N, Olson EN. MicroRNAs flex their muscles. Trends Genet. 2008;24:159–66. - PubMed
-
- Hammond SM. Dicing and slicing: the core machinery of the RNA interference pathway. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5822–9. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, Chen CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Dorn GW., 2nd Therapeutic potential of microRNAs in heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep. 12:209–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

