Bayesian analysis of biogeography when the number of areas is large
- PMID: 23736102
- PMCID: PMC4064008
- DOI: 10.1093/sysbio/syt040
Bayesian analysis of biogeography when the number of areas is large
Abstract
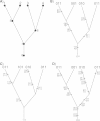
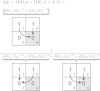
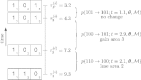
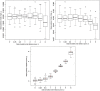
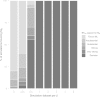
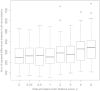
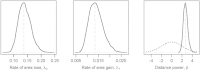
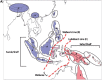
Historical biogeography is increasingly studied from an explicitly statistical perspective, using stochastic models to describe the evolution of species range as a continuous-time Markov process of dispersal between and extinction within a set of discrete geographic areas. The main constraint of these methods is the computational limit on the number of areas that can be specified. We propose a Bayesian approach for inferring biogeographic history that extends the application of biogeographic models to the analysis of more realistic problems that involve a large number of areas. Our solution is based on a "data-augmentation" approach, in which we first populate the tree with a history of biogeographic events that is consistent with the observed species ranges at the tips of the tree. We then calculate the likelihood of a given history by adopting a mechanistic interpretation of the instantaneous-rate matrix, which specifies both the exponential waiting times between biogeographic events and the relative probabilities of each biogeographic change. We develop this approach in a Bayesian framework, marginalizing over all possible biogeographic histories using Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC). Besides dramatically increasing the number of areas that can be accommodated in a biogeographic analysis, our method allows the parameters of a given biogeographic model to be estimated and different biogeographic models to be objectively compared. Our approach is implemented in the program, BayArea.
Figures


References
-
- Brown G., Nelson G., Ladiges P.Y. Historical biogeography of Rhododendron Section Vireya and the Malesian Archipelago. J. Biogeogr. 2006;33:1929–1944.
-
- Buerki S., Forest F., Alvarez N., Nylander J.A.A., Arrigo N., Sanmartín I. An evaluation of new parsimony-based versus parametric inference methods in biogeography: a case study using the globally distributed plant family Sapindaceae. J Biogeog. 2011;38:531–550.
-
- Carlquist S. The biota of long-distance dispersal: I. Principles of dispersal and evolution. Q. Rev. Biol. 1966;41:247–270. - PubMed
-
- Clark J.R., Ree R.H., Alfaro M.E., King M.G., Wagner W.L., Roalson E.H. A comparative study in ancestral range reconstruction methods: retracing the uncertain histories of insular lineages. Syst. Biol. 2008;57:693–707. - PubMed
-
- Dickey J. The weighted likelihood ratio, linear hypotheses on normal location parameters. Ann. Stat. 1971;42:204–223.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

