Subtilomycin: a new lantibiotic from Bacillus subtilis strain MMA7 isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans
- PMID: 23736764
- PMCID: PMC3721211
- DOI: 10.3390/md11061878
Subtilomycin: a new lantibiotic from Bacillus subtilis strain MMA7 isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans
Abstract
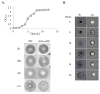
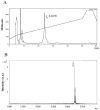
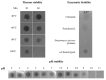
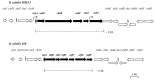
Bacteriocins are attracting increased attention as an alternative to classic antibiotics in the fight against infectious disease and multidrug resistant pathogens. Bacillus subtilis strain MMA7 isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans displays a broad spectrum antimicrobial activity, which includes Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens, as well as several pathogenic Candida species. This activity is in part associated with a newly identified lantibiotic, herein named as subtilomycin. The proposed biosynthetic cluster is composed of six genes, including protein-coding genes for LanB-like dehydratase and LanC-like cyclase modification enzymes, characteristic of the class I lantibiotics. The subtilomycin biosynthetic cluster in B. subtilis strain MMA7 is found in place of the sporulation killing factor (skf) operon, reported in many B. subtilis isolates and involved in a bacterial cannibalistic behaviour intended to delay sporulation. The presence of the subtilomycin biosynthetic cluster appears to be widespread amongst B. subtilis strains isolated from different shallow and deep water marine sponges. Subtilomycin possesses several desirable industrial and pharmaceutical physicochemical properties, including activity over a wide pH range, thermal resistance and water solubility. Additionally, the production of the lantibiotic subtilomycin could be a desirable property should B. subtilis strain MMA7 be employed as a probiotic in aquaculture applications.
Figures


References
-
- Kennedy J., Baker P., Piper C., Cotter P.D., Walsh M., Mooij M.J., Bourke M.B., Rea M.C., O’Connor P.M., Ross R.P. Isolation and analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans collected from Irish waters. Mar. Biotechnol. (NY) 2009;11:384–396. doi: 10.1007/s10126-008-9154-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

