The efficacy of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depressive and anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of direct comparisons
- PMID: 23737423
- PMCID: PMC3683266
- DOI: 10.1002/wps.20038
The efficacy of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depressive and anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of direct comparisons
Abstract
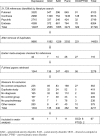
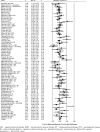
Although psychotherapy and antidepressant medication are efficacious in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders, it is not known whether they are equally efficacious for all types of disorders, and whether all types of psychotherapy and antidepressants are equally efficacious for each disorder. We conducted a meta-analysis of studies in which psychotherapy and antidepressant medication were directly compared in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders. Systematic searches in bibliographical databases resulted in 67 randomized trials, including 5,993 patients that met inclusion criteria, 40 studies focusing on depressive disorders and 27 focusing on anxiety disorders. The overall effect size indicating the difference between psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy after treatment in all disorders was g=0.02 (95% CI: -0.07 to 0.10), which was not statistically significant. Pharmacotherapy was significantly more efficacious than psychotherapy in dysthymia (g=0.30), and psychotherapy was significantly more efficacious than pharmacotherapy in obsessive-compulsive disorder (g=0.64). Furthermore, pharmacotherapy was significantly more efficacious than non-directive counseling (g=0.33), and psychotherapy was significantly more efficacious than pharmacotherapy with tricyclic antidepressants (g=0.21). These results remained significant when we controlled for other characteristics of the studies in multivariate meta-regression analysis, except for the differential effects in dysthymia, which were no longer statistically significant.
Copyright © 2013 World Psychiatric Association.
Figures
References
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. National Comorbidity Survey Replication. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) JAMA. 2003;289:3095–105. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Berto P, D'Ilario D, Ruffo P, et al. Depression: cost-of-illness studies in the international literature: a review. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2000;3:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg PE, Birnbaum HG. The economic burden of depression in the US: societal and patient perspectives. Exp Opin Pharmacother. 2005;6:369–76. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous