Interactions with iridophores and the tissue environment required for patterning melanophores and xanthophores during zebrafish adult pigment stripe formation
- PMID: 23737760
- PMCID: PMC3667786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003561
Interactions with iridophores and the tissue environment required for patterning melanophores and xanthophores during zebrafish adult pigment stripe formation
Abstract
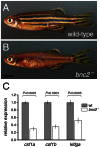
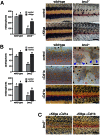
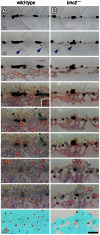
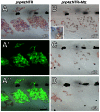
Skin pigment patterns of vertebrates are a classic system for understanding fundamental mechanisms of morphogenesis, differentiation, and pattern formation, and recent studies of zebrafish have started to elucidate the cellular interactions and molecular mechanisms underlying these processes. In this species, horizontal dark stripes of melanophores alternate with light interstripes of yellow or orange xanthophores and iridescent iridophores. We showed previously that the highly conserved zinc finger protein Basonuclin-2 (Bnc2) is required in the environment in which pigment cells reside to promote the development and maintenance of all three classes of pigment cells; bnc2 mutants lack body stripes and interstripes. Previous studies also revealed that interactions between melanophores and xanthophores are necessary for organizing stripes and interstripes. Here we show that bnc2 promotes melanophore and xanthophore development by regulating expression of the growth factors Kit ligand a (Kitlga) and Colony stimulating factor-1 (Csf1), respectively. Yet, we found that rescue of melanophores and xanthophores was insufficient for the recovery of stripes in the bnc2 mutant. We therefore asked whether bnc2-dependent iridophores might contribute to stripe and interstripe patterning as well. We found that iridophores themselves express Csf1, and by ablating iridophores in wild-type and mutant backgrounds, we showed that iridophores contribute to organizing both melanophores and xanthophores during the development of stripes and interstripes. Our results reveal an important role for the cellular environment in promoting adult pigment pattern formation and identify new components of a pigment-cell autonomous pattern-generating system likely to have broad implications for understanding how pigment patterns develop and evolve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
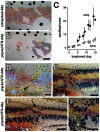
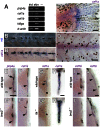
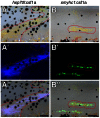
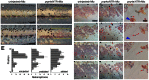

Comment in
-
Black, yellow, or silver: which one leads skin pattern formation?Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015 Jan;28(1):2-4. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12328. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015. PMID: 25367546 No abstract available.
References
-
- Price AC, Weadick CJ, Shim J, Rodd FH (2008) Pigments, Patterns, and Fish Behavior. Zebrafish 5: 297–307. - PubMed
-
- Streelman JT, Peichel CL, Parichy DM (2007) Developmental genetics of adaptation in fishes: The case of novelty. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics 38: 655–681.
-
- Houde AE (1997) Sex, Color, and Mate Choice in Guppies. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
-
- Kelsh RN (2004) Genetics and evolution of pigment patterns in fish. Pigment Cell Res 17: 326–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

