Antiteratogenic Effects of β-Carotene in Cultured Mouse Embryos Exposed to Nicotine
- PMID: 23737837
- PMCID: PMC3662118
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/575287
Antiteratogenic Effects of β-Carotene in Cultured Mouse Embryos Exposed to Nicotine
Abstract
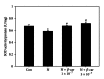
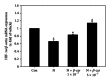
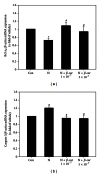
After maternal intake, nicotine crosses the placental barrier and causes severe embryonic disorders and fetal death. In this study, we investigated whether β -carotene has a beneficial effect against nicotine-induced teratogenesis in mouse embryos (embryonic day 8.5) cultured for 48 h in a whole embryo culture system. Embryos exposed to nicotine (1 mM) exhibited severe morphological anomalies and apoptotic cell death, as well as increased levels of TNF- α , IL-1 β , and caspase 3 mRNAs, and lipid peroxidation. The levels of cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase (SOD), mitochondrial manganese-dependent SOD, cytosolic glutathione peroxidase (GPx), phospholipid hydroperoxide GPx, hypoxia inducible factor 1 α , and Bcl-x L mRNAs decreased, and SOD activity was reduced compared to the control group. However, when β -carotene (1 × 10(-7) or 5 × 10(-7) μM) was present in cultures of embryos exposed to nicotine, these parameters improved significantly. These findings indicate that β -carotene effectively protects against nicotine-induced teratogenesis in mouse embryos through its antioxidative, antiapoptotic, and anti-inflammatory activities.
Figures





References
-
- Lambers DS, Clark KE. The maternal and fetal physiologic effects of nicotine. Seminars in Perinatology. 1996;20(2):115–126. - PubMed
-
- Comhair SAA, Erzurum SC. Antioxidant responses to oxidant-mediated lung diseases. American Journal of Physiology. 2002;283(2):L246–L255. - PubMed
-
- Ornoy A. Embryonic oxidative stress as a mechanism of teratogenesis with special emphasis on diabetic embryopathy. Reproductive Toxicology. 2007;24(1):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Cogswell ME, Weisberg P, Spong C. Cigarette smoking, alcohol use and adverse pregnancy outcomes: implications for micronutrient supplementation. Journal of Nutrition. 2003;133:1722S–1731S. - PubMed
-
- Lin C, Yon JM, Jung AY, et al. Resveratrol prevents nicotine-induced teratogenesis in cultured mouse embryos. Reproductive Toxicology. 2012;34(3):340–360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

