Plasma lipoproteins as mediators of the oxidative stress induced by UV light in human skin: a review of biochemical and biophysical studies on mechanisms of apolipoprotein alteration, lipid peroxidation, and associated skin cell responses
- PMID: 23738035
- PMCID: PMC3655670
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/285825
Plasma lipoproteins as mediators of the oxidative stress induced by UV light in human skin: a review of biochemical and biophysical studies on mechanisms of apolipoprotein alteration, lipid peroxidation, and associated skin cell responses
Abstract
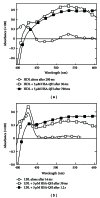
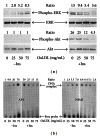
There are numerous studies concerning the effect of UVB light on skin cells but fewer on other skin components such as the interstitial fluid. This review highlights high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) as important targets of UVB in interstitial fluid. Tryptophan residues are the sole apolipoprotein residues absorbing solar UVB. The UVB-induced one-electron oxidation of Trp produces (•)Trp and (•)O2 (-) radicals which trigger lipid peroxidation. Immunoblots from buffered solutions or suction blister fluid reveal that propagation of photooxidative damage to other residues such as Tyr or disulfide bonds produces intra- and intermolecular bonds in apolipoproteins A-I, A-II, and B100. Partial repair of phenoxyl tyrosyl radicals (TyrO(•)) by α -tocopherol is observed with LDL and HDL on millisecond or second time scales, whereas limited repair of α -tocopherol by carotenoids occurs in only HDL. More effective repair of Tyr and α -tocopherol is observed with the flavonoid, quercetin, bound to serum albumin, but quercetin is less potent than new synthetic polyphenols in inhibiting LDL lipid peroxidation or restoring α -tocopherol. The systemic consequences of HDL and LDL oxidation and the activation and/or inhibition of signalling pathways by oxidized LDL and their ability to enhance transcription factor DNA binding activity are also reviewed.
Figures





References
-
- Epstein JH. Photocarcinogenesis, skin cancer, and aging. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1983;9(4):487–502. - PubMed
-
- Nishi J, Ogura R, Sugiyama M, Hidaka T, Kohno M. Involvement of active oxygen in lipid peroxide radical reaction of epidermal homogenate following ultraviolet light exposure. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1991;97(1):115–119. - PubMed
-
- Tyrrell RM. UVA (320-380 nm) radiation as an oxidative stress. In: Sies H, editor. Oxidative Stress. Oxidants and Antioxidants. London, UK: Academic Press; 1991. pp. 57–83.
-
- Morlière P, Moysan A, Tirache I. Action spectrum for UV-induced lipid peroxidation in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1995;19(3):365–371. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto K, Sugiyama M, Ogura R. Non-dimer DNA damage in Chinese hamster V-79 cells exposed to ultraviolet-B light. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 1991;54(3):389–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

