Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants
- PMID: 23738047
- PMCID: PMC3657405
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/956792
Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants
Abstract
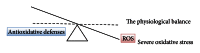
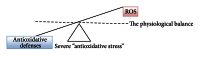
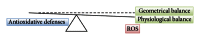
Free radical damage is linked to formation of many degenerative diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, cataracts, and aging. Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation can induce oxidative stress, leading to cell damage that can culminate in cell death. Therefore, cells have antioxidant networks to scavenge excessively produced ROS. The balance between the production and scavenging of ROS leads to homeostasis in general; however, the balance is somehow shifted towards the formation of free radicals, which results in accumulated cell damage in time. Antioxidants can attenuate the damaging effects of ROS in vitro and delay many events that contribute to cellular aging. The use of multivitamin/mineral supplements (MVMs) has grown rapidly over the past decades. Some recent studies demonstrated no effect of antioxidant therapy; sometimes the intake of antioxidants even increased mortality. Oxidative stress is damaging and beneficial for the organism, as some ROS are signaling molecules in cellular signaling pathways. Lowering the levels of oxidative stress by antioxidant supplements is not beneficial in such cases. The balance between ROS and antioxidants is optimal, as both extremes, oxidative and antioxidative stress, are damaging. Therefore, there is a need for accurate determination of individual's oxidative stress levels before prescribing the supplement antioxidants.
Figures


References
-
- Riley PA. Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. International Journal of Radiation Biology. 1994;65(1):27–33. - PubMed
-
- Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC, Cross CE. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: where are we now? Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine. 1992;119(6):598–620. - PubMed
-
- Poljsak B, Jamnik P, Raspor P, Pesti M. Oxidation-antioxidation-reduction processes in the cell: impacts of environmental pollution. In: Jerome N, editor. Encyclopedia of Environmental Health. Elsevier; 2011. pp. 300–306.
-
- Gilca M, Stoian I, Atanasiu V, Virgolici B. The oxidative hypothesis of senescence. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine. 2007;53(3):207–213. - PubMed
-
- Gutteridge JMC. Free radicals in disease processes: a compilation of cause and consequence. Free Radical Research Communications. 1993;19(3):141–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

