Employment of a needs assessment survey to shape a novel web-based pediatric rheumatology curriculum for primary care providers
- PMID: 23738823
- PMCID: PMC3680051
- DOI: 10.1186/1546-0096-11-26
Employment of a needs assessment survey to shape a novel web-based pediatric rheumatology curriculum for primary care providers
Abstract
Background: Pediatric rheumatology faces many challenges due to the shortage of board certified physicians in the field and the imbalance in their geographic distribution. This shortage has required primary care physicians and adult rheumatologists to assume the care of children with rheumatologic diseases, though these physicians report significant discomfort doing so. We are addressing this issue through the development of a novel web-based curriculum aimed at primary care physicians.
Methods: We pursued a needs assessment survey of Vanderbilt pediatric residency graduates (1981-2010) working in primary care. Our goals were to understand their perceptions of what the needs are and what educational interventions would be most effective.
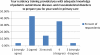
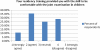
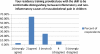
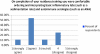
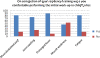
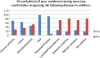
Results: Of 152 surveys sent successfully via Survey Monkey, we received 28 responses (18.4%). Responses suggest there to be a discrepancy between physicians' general assessment of their training and their self-reported ability to recognize specific diseases. Nearly 80% of respondents felt that additional education in pediatric rheumatology would improve their ability to co-manage children with the rheumatologist. Action plans for common rheumatologic complaints and potential emergencies were thought to be of potential benefit by a majority of respondents.
Conclusions: We will utilize our survey results to develop a learner centered curriculum to have the highest positive impact in assisting primary care providers in caring for children with rheumatologic diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Availability of pediatric rheumatology training in United States pediatric residencies.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec 15;55(6):836-42. doi: 10.1002/art.22347. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17139658
-
Pediatric Rheumatology Curriculum for the Pediatrics Resident: A Case-Based Approach to Learning.MedEdPORTAL. 2018 Oct 26;14:10767. doi: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.10767. MedEdPORTAL. 2018. PMID: 30800967 Free PMC article.
-
A rheumatology curriculum in Pakistan for empowering family physicians and fighting disability.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;39(3):681-687. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04797-7. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31848913
-
Access to pediatric rheumatology care in the United States.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Dec 15;49(6):759-65. doi: 10.1002/art.11462. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14673961 Review.
-
Workforce Trends in Rheumatology.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019 Feb;45(1):13-26. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2018.09.002. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30447742 Review.
Cited by
-
VIRTUAL LEARNING ENVIRONMENT IN PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGY FOR PEDIATRIC RESIDENTS.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2020 Jan 13;38:e2018189. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2020/38/2018189. eCollection 2020. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31939511 Free PMC article.
-
A mixed methods evaluation of the Paediatric Musculoskeletal Matters (PMM) online portfolio.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021 Jun 9;19(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12969-021-00567-5. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34108019 Free PMC article.
-
pGALS - paediatric Gait Arms Legs and Spine: a simple examination of the musculoskeletal system.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2013 Nov 12;11(1):44. doi: 10.1186/1546-0096-11-44. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2013. PMID: 24219838 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric musculoskeletal matters (pmm)--collaborative development of an online evidence based interactive learning tool and information resource for education in paediatric musculoskeletal medicine.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2016 Jan 5;14(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12969-015-0062-4. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2016. PMID: 26728031 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Rheumatology Laboratory Studies Among Primary Pediatricians.Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2016 Dec;55(14):1279-1288. doi: 10.1177/0009922815624902. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26755273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freed GL. et al.Comparing the self-reported referral and management preferences of pediatricians and family physicians for children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2700–2704. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

