The MID1 E3 ligase catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Alpha4 (α4), a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A): novel insights into MID1-mediated regulation of PP2A
- PMID: 23740247
- PMCID: PMC3774402
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.481093
The MID1 E3 ligase catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Alpha4 (α4), a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A): novel insights into MID1-mediated regulation of PP2A
Abstract
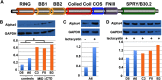
Alpha4 (α4) is a key regulator of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and mTOR in steps essential for cell-cycle progression. α4 forms a complex with PP2A and MID1, a microtubule-associated ubiquitin E3 ligase that facilitates MID1-dependent regulation of PP2A and the dephosphorylation of MID1 by PP2A. Ectopic overexpression of α4 is associated with hepatocellular carcinomas, breast cancer, and invasive adenocarcinomas. Here, we provide data suggesting that α4 is regulated by ubiquitin-dependent degradation mediated by MID1. In cells stably expressing a dominant-negative form of MID1, significantly elevated levels of α4 were observed. Treatment of cells with the specific proteasome inhibitor, lactacystin, resulted in a 3-fold increase in α4 in control cells and a similar level in mutant cells. Using in vitro assays, individual MID1 E3 domains facilitated monoubiquitination of α4, whereas full-length MID1 as well as RING-Bbox1 and RING-Bbox1-Bbox2 constructs catalyzed its polyubiquitination. In a novel non-biased functional screen, we identified a leucine to glutamine substitution at position 146 within Bbox1 that abolished MID1-α4 interaction and the subsequent polyubiquitination of α4, indicating that direct binding to Bbox1 was necessary for the polyubiquitination of α4. The mutant had little impact on the RING E3 ligase functionality of MID1. Mass spectrometry data confirmed Western blot analysis that ubiquitination of α4 occurs only within the last 105 amino acids. These novel findings identify a new role for MID1 and a mechanism of regulation of α4 that is likely to impact the stability and activity level of PP2Ac.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Signaling; Cellular Immune Response; E3 Ubiquitin Ligase; PP2A; Protein Degradation; Ubiquitination.
Figures





References
-
- Chuang E., Fisher T. S., Morgan R. W., Robbins M. D., Duerr J. M., Vander Heiden M. G., Gardner J. P., Hambor J. E., Neveu M. J., Thompson C. B. (2000) The CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors associate with the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A. Immunity 13, 313–322 - PubMed
-
- Inui S., Kuwahara K., Mizutani J., Maeda K., Kawai T., Nakayasu H., Sakaguchi N. (1995) Molecular cloning of a cDNA clone encoding a phosphoprotein component related to the Ig receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Immunol. 154, 2714–2723 - PubMed
-
- Inui S., Sanjo H., Maeda K., Yamamoto H., Miyamoto E., Sakaguchi N. (1998) Ig receptor binding protein 1 (α4) is associated with a rapamycin-sensitive signal transduction in lymphocytes through direct binding to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Blood 92, 539–546 - PubMed
-
- Onda M., Inui S., Maeda K., Suzuki M., Takahashi E., Sakaguchi N. (1997) Expression and chromosomal localization of the human α4/IGBP1 gene, the structure of which is closely related to the yeast TAP42 protein of the rapamycin-sensitive signal transduction pathway. Genomics 46, 373–378 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

