Application of a PEG precipitation method for solubility screening: a tool for developing high protein concentration formulations
- PMID: 23740802
- PMCID: PMC3832048
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2289
Application of a PEG precipitation method for solubility screening: a tool for developing high protein concentration formulations
Abstract
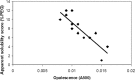
Previous publications demonstrated that the extrapolated solubility by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation method (Middaugh et al., J Biol Chem 1979; 254:367-370; Juckes, Biochim Biophys Acta 1971; 229:535-546; Foster et al., Biochim Biophys Acta 1973; 317:505; Mahadevan and Hall, AIChE J 1990; 36:1517-1528; Stevenson and Hageman, Pharm Res 1995; 12:1671-1676) has a strong correlation to experimentally measured solubility of proteins. Here, we explored the utility of extrapolated solubility as a method to compare multiple protein drug candidates when nonideality of a highly soluble protein prohibits accurate quantitative solubility prediction. To achieve high efficiency and reduce the amount of protein required, the method is miniaturized to microwell plate format for high-throughput screening application. In this simplified version of the method, comparative solubility of proteins can be obtained without the need of concentration measurement of the supernatant following the precipitation step in the conventional method. The monoclonal antibodies with the lowest apparent solubilities determined by this method are the most difficult to be concentrated, indicating a good correlation between the prediction and empirical observations. This study also shows that the PEG precipitation method gives results for opalescence prediction that favorably compares to experimentally determined opalescence levels at high concentration. This approach may be useful in detecting proteins with potential solubility and opalescence problems prior to the time-consuming and expensive development process of high concentration formulation.
Keywords: high-throughput screen; monoclonal antibody; polyethylene glycol; solubility; volume exclusion.
© 2013 The Protein Society.
Figures



References
-
- Shire SJ, Shahrokh Z, Liu J. Challenges in the development of high protein concentration formulations. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:1390–1402. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell GW, Ritchie DM, Masucci JA, Hageman W, Yan Z. The new pre-preclinical paradigm: compound optimization in early and late phase drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem. 2001;1:353–366. - PubMed
-
- Middaugh CR, Tisel WA, Haire RN, Rosenberg A. Determination of the apparent thermodynamic activities of saturated protein solutions. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:367–370. - PubMed
-
- Juckes IRM. Fractionation of proteins and viruses with polyethylene glycol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;229:535–546. - PubMed
-
- Foster PR, Dunhill P, Lilly MD. The precipitation of enzymes from cell extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by polyethylene-glycol. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1973;317:505. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

