The kinase activity of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated interferes with adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication
- PMID: 23740981
- PMCID: PMC3719797
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00376-13
The kinase activity of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated interferes with adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication
Abstract
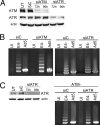
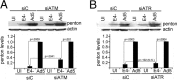
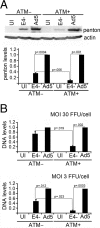
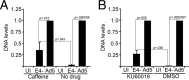
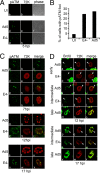
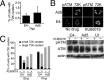
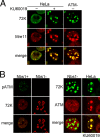
Adenovirus (Ad) mutants that lack early region 4 (E4) are unable to produce the early regulatory proteins that normally inactivate the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 (MRN) sensor complex, which is a critical component for the ability of cells to respond to DNA damage. E4 mutant infection therefore activates a DNA damage response, which in turn interferes with a productive viral infection. MRN complex proteins localize to viral DNA replication centers in E4 mutant-infected cells, and this complex is critical for activating the kinases ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM and Rad3-related (ATR), which phosphorylate numerous substrates important for DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoint activation, and apoptosis. E4 mutant growth defects are substantially rescued in cells lacking an intact MRN complex. We have assessed the role of the downstream ATM and ATR kinases in several MRN-dependent E4 mutant phenotypes. We did not identify a role for either ATM or ATR in "repair" of E4 mutant genomes to form concatemers. ATR was also not observed to contribute to E4 mutant defects in late protein production. In contrast, the kinase activity of ATM was important for preventing efficient E4 mutant DNA replication and late gene expression. Our results suggest that the MRN complex interferes with E4 mutant DNA replication at least in part through its ability to activate ATM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Localization of the kinase Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated to Adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication centers is important for its inhibitory effect on viral DNA accumulation.Virology. 2019 Jan 15;527:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Virology. 2019. PMID: 30453211 Free PMC article.
-
Mislocalization of the MRN complex prevents ATR signaling during adenovirus infection.EMBO J. 2009 Mar 18;28(6):652-62. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.15. Epub 2009 Feb 5. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19197236 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements of the C terminus of Nbs1 in suppressing adenovirus DNA replication and promoting concatemer formation.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8362-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00900-08. Epub 2008 Jun 18. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18562516 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NBS1 in the modulation of PIKK family proteins ATM and ATR in the cellular response to DNA damage.Cancer Lett. 2006 Nov 8;243(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.01.026. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 16530324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM and the Mre11 complex combine to recognize and signal DNA double-strand breaks.Oncogene. 2007 Dec 10;26(56):7749-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210880. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 18066087 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenovirus E4-ORF3 Targets PIAS3 and Together with E1B-55K Remodels SUMO Interactions in the Nucleus and at Virus Genome Replication Domains.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10260-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01091-15. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26223632 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Oncolytic Adenovirus with Radiation-A Paradigm for the Future of Radiosensitization.Front Oncol. 2017 Jul 24;7:153. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00153. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28791251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biphasic Functional Interaction between the Adenovirus E4orf4 Protein and DNA-PK.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e01365-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01365-18. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30842317 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of the kinase Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated to Adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication centers is important for its inhibitory effect on viral DNA accumulation.Virology. 2019 Jan 15;527:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Virology. 2019. PMID: 30453211 Free PMC article.
-
En Guard! The Interactions between Adenoviruses and the DNA Damage Response.Viruses. 2020 Sep 7;12(9):996. doi: 10.3390/v12090996. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32906746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

