Vasoactive intestinal peptide produces long-lasting changes in neural activity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
- PMID: 23741043
- PMCID: PMC4073931
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00114.2013
Vasoactive intestinal peptide produces long-lasting changes in neural activity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
Abstract
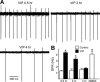
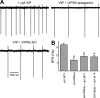
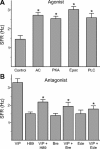
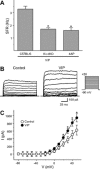
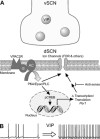
The neuropeptide vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is expressed at high levels in the neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). While VIP is known to be important to the input and output pathways from the SCN, the physiological effects of VIP on electrical activity of SCN neurons are not well known. Here the impact of VIP on firing rate of SCN neurons was investigated in mouse slice cultures recorded during the night. The application of VIP produced an increase in electrical activity in SCN slices that lasted several hours after treatment. This is a novel mechanism by which this peptide can produce long-term changes in central nervous system physiology. The increase in action potential frequency was blocked by a VIP receptor antagonist and lost in a VIP receptor knockout mouse. In addition, inhibitors of both the Epac family of cAMP binding proteins and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) blocked the induction by VIP. The persistent increase in spike rate following VIP application was not seen in SCN neurons from mice deficient in Kv3 channel proteins and was dependent on the clock protein PER1. These findings suggest that VIP regulates the long-term firing rate of SCN neurons through a VIPR2-mediated increase in the cAMP pathway and implicate the fast delayed rectifier (FDR) potassium currents as one of the targets of this regulation.
Keywords: VIP; circadian system; fast delayed rectifier; potassium; suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama M, Kouzu Y, Takahashi S, Wakamatsu H, Moriya T, Maetani M, Watanabe S, Tei H, Sakaki Y, Shibata S. Inhibition of light- or glutamate-induced mPer1 expression represses the phase shifts into the mouse circadian locomotor and suprachiasmatic firing rhythms. J Neurosci 19: 1115–1121, 1999 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baranauskas G. Ionic channel function in action potential generation: current perspective. Mol Neurobiol 35: 129–150, 2007 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

