Ex-PRESS implantation versus trabeculectomy in uncontrolled glaucoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 23741296
- PMCID: PMC3669314
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063591
Ex-PRESS implantation versus trabeculectomy in uncontrolled glaucoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of Ex-PRESS implantation (Ex-Press) compared with trabeculectomy (Trab) in the treatment of patients with uncontrolled glaucoma.
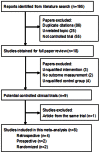
Methods: A comprehensive literature meta-analysis was performed according to the Cochrane Collaboration methodology to identify controlled clinical trials comparing Ex-Press with Trab. Efficacy estimates were measured by weight mean difference (WMD) for the percentage intraocular pressure (IOP) reduction from baseline to end-point, odds ratio (OR) for complete success, and qualified success rates. Tolerability estimates were measured by OR for adverse events. All outcomes were reported with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Data were synthesized by Stata 11.0 SE for Windows.
Results: Eight controlled clinical trials meeting the predefined criteria were included in the meta-analysis. A total of 605 eyes from 559 patients with medically uncontrolled glaucoma were included. The weighted mean difference of the percentage IOP reduction from baseline was 2.33 (95% confidence interval: -2.59-7.24) when comparing Ex-Press with Trab. Ex-Press was associated with numerically greater, but nonsignificant, IOP lowering efficacy than Trab. The pooled odds ratio comparing Ex-Press with Trab were 0.93 (0.39, 2.23) for the complete success rate and 1.00 (0.39, 2.56) for the qualified success rate. Ex-Press was associated with a significantly lower frequency of hypotony and hyphema than Trab, with pooled ORs of 0.29 (0.13, 0.65) and 0.36 (0.13, 0.97), respectively.
Conclusion: Ex-Press was associated with equivalent efficacy to Trab in lowering IOP. Comparable proportions of patients reached the IOP target with Ex-Press and Trab. Ex-Press was better tolerated than Trab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mosaed S, Minckler DS (2010) Aqueous shunts in the treatment of glaucoma. Expert Rev Med Devices 7: 661–666. - PubMed
-
- Hendrick AM, Kahook MY (2008) Ex-PRESS mini glaucoma shunt: surgical technique and review of clinical experience. Expert Rev Med Devices 5: 673–677. - PubMed
-
- Dahan E, Carmichael TR (2005) Implantation of a miniature glaucoma device under a scleral flap. J Glaucoma 14: 98–102. - PubMed
-
- Rouse JM, Sarkisian SJ (2012) Mini-drainage devices: the Ex-PRESS Mini-Glaucoma Device. Dev Ophthalmol 50: 90–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical