Hydrogen sulfide prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of epithelial sodium channel through a PTEN/PI(3,4,5)P3 dependent pathway
- PMID: 23741314
- PMCID: PMC3669336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064304
Hydrogen sulfide prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of epithelial sodium channel through a PTEN/PI(3,4,5)P3 dependent pathway
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(10). doi:10.1371/annotation/1cc3a25b-dc35-4d2a-8465-b11916f2e863
Abstract
Sodium reabsorption through the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) at the distal segment of the kidney plays an important role in salt-sensitive hypertension. We reported previously that hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulates ENaC in A6 distal nephron cells via elevation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3) in the apical membrane. Here we report that H2S can antagonize H2O2-induced activation of ENaC in A6 cells. Our cell-attached patch-clamp data show that ENaC open probability (PO ) was significantly increased by exogenous H2O2, which is consistent with our previous finding. The aberrant activation of ENaC induced by exogenous H2O2 was completely abolished by H2S (0.1 mM NaHS). Pre-treatment of A6 cells with H2S slightly decreased ENaC P(O); however, in these cells H2O2 failed to elevate ENaC PO . Confocal microscopy data show that application of exogenous H2O2 to A6 cells significantly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level and induced accumulation of PI(3,4,5)P3 in the apical compartment of the cell membrane. These effects of exogenous H2O2 on intracellular ROS levels and on apical PI(3,4,5)P3 levels were almost completely abolished by treatment of A6 cells with H2S. In addition, H2S significantly inhibited H2O2-induced oxidative inactivation of the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) which is a negative regulator of PI(3,4,5)P3. Moreover, BPV(pic), a specific inhibitor of PTEN, elevated PI(3,4,5)P3 and ENaC activity in a manner similar to that of H2O2 in A6 cells. Our data show, for the first time, that H2S prevents H2O2-induced activation of ENaC through a PTEN-PI(3,4,5)P3 dependent pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


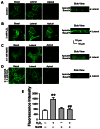
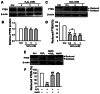
 P<0.05 compared with 0.3 mM H2O2 treatment group; ##
P<0.01 compared with H2O2 treatment group.
P<0.05 compared with 0.3 mM H2O2 treatment group; ##
P<0.01 compared with H2O2 treatment group.

Similar articles
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Advanced Glycation End-Products Induced Activation of the Epithelial Sodium Channel.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:976848. doi: 10.1155/2015/976848. Epub 2015 May 11. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26078825 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide stimulates the epithelial sodium channel through a phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 16;286(37):32444-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.254102. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21795700 Free PMC article.
-
Fulvene-5 inhibition of Nadph oxidases attenuates activation of epithelial sodium channels in A6 distal nephron cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Oct 1;305(7):F995-F1005. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00098.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23863470 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Peroxide and Sodium Transport in the Lung and Kidney.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9512807. doi: 10.1155/2016/9512807. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27073804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGK1: aldosterone-induced relay of Na+ transport regulation in distal kidney nephron cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2003;13(1):21-8. doi: 10.1159/000070246. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12649599 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogen Sulfide in Hypertension and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 11;19(5):1438. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051438. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29751631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates epithelial sodium channels in endothelial cells of mouse thoracic aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(8):1318-1328. doi: 10.1111/bph.13853. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28480509 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide Donors in Common Kidney Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 19;11:564281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.564281. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33364941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and vascular regulation - An update.J Adv Res. 2020 May 16;27:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.05.007. eCollection 2021 Jan. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33318869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial Na + Channels Function as Extracellular Sensors.Compr Physiol. 2024 Mar 29;14(2):1-41. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c230015. Compr Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39109974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warnock DG (2001) Liddle syndrome: genetics and mechanisms of Na+ channel defects. Am J Med Sci 322: 302–307. - PubMed
-
- Mori T, O’Connor PM, Abe M, Cowley AW Jr (2007) Enhanced superoxide production in renal outer medulla of Dahl salt-sensitive rats reduces nitric oxide tubular-vascular cross-talk. Hypertension 49: 1336–1341. - PubMed
-
- Taylor NE, Cowley AW Jr (2005) Effect of renal medullary H2O2 on salt-induced hypertension and renal injury. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289: R1573–1579. - PubMed
-
- Taylor NE, Glocka P, Liang M, Cowley AW Jr (2006) NADPH oxidase in the renal medulla causes oxidative stress and contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats. Hypertension 47: 692–698. - PubMed
-
- Yu L, Bao HF, Self JL, Eaton DC, Helms MN (2007) Aldosterone-induced increases in superoxide production counters nitric oxide inhibition of epithelial Na channel activity in A6 distal nephron cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293: F1666–1677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

